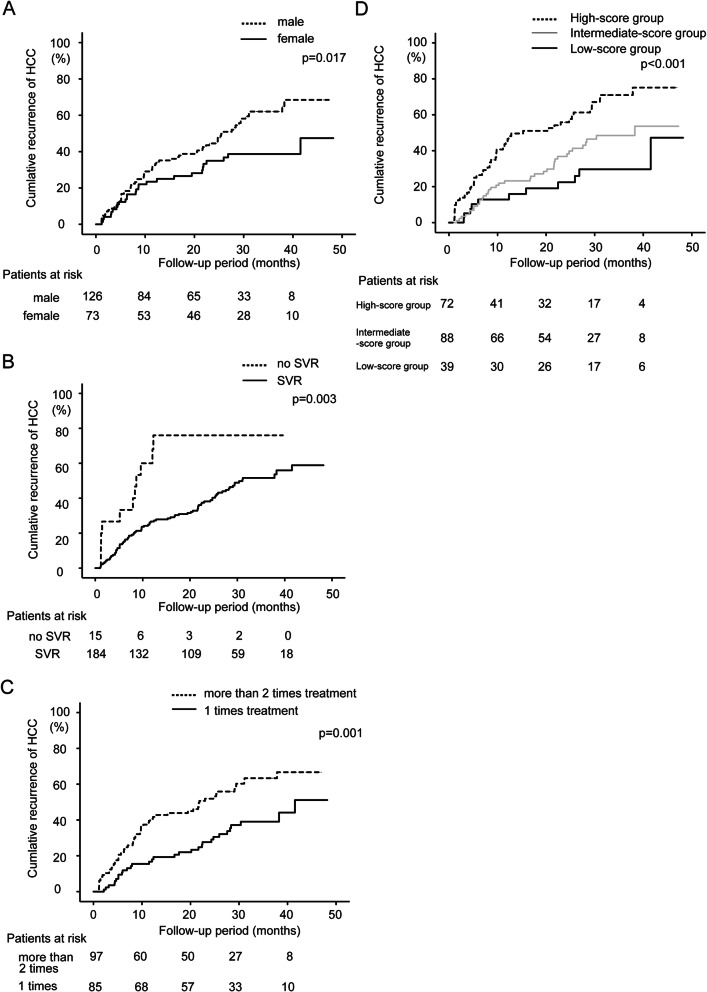
Fig. 2.
Comparison of cumulative HCC recurrence (%) by sex (A). Cumulative HCC recurrence is significantly higher in males than in females, according to the log-rank test (p = 0.017). Comparison of cumulative HCC recurrence (%) by sustained virological response (SVR) achievement (B). Cumulative HCC recurrence is significantly higher in the ‘no SVR’ group than in the group with SVR according to the log-rank test (p = 0.003). Comparison of cumulative HCC recurrence (%) between the group with more than two past HCC treatments and the group with only one HCC treatment (C). Cumulative HCC recurrence is significantly higher in the group with more than two past HCC treatments according to the log-rank test (p = 0.001). Cumulative recurrence (%) of HCC according to the score combining sex, SVR achievement, and number of past HCC treatments (D). Study patients are grouped based on these scores: 0 points, low-risk group (n = 39); 1 or 2 points, intermediate-risk group (n = 88); and 3 points, high-risk group (n = 72). Cumulative HCC recurrence increases significantly with higher scores (p < 0.001)