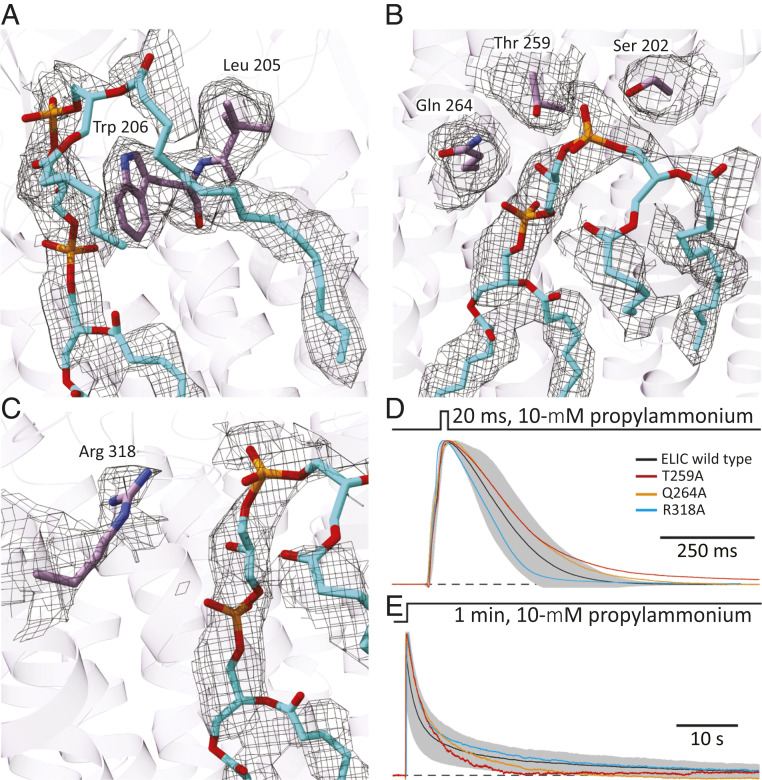
Fig. 5.
Cardiolipin-binding site in unliganded ELIC. (A–C) Atomic model of cardiolipin and protein atoms within 5 Å of the phosphate–glycerol–phosphate polar head group. The corresponding densities are also displayed (display level = 0.7). Ser-202, Leu-205, and Trp-206 are in transmembrane α-helix M1; Thr-259, in the M2–M3 linker; Gln-264, in M3; and Arg-318, in M4. Phospholipid and amino-acid atoms are shown in stick representation with carbons colored cyan and purple, respectively. The molecular images were prepared with Chimera X (42). (D and E) Outward currents recorded in the whole-cell configuration from HEK-293 cells transiently transfected with wild-type ELIC or one of the indicated alanine mutants in response to short and long applications of saturating (10 mM) propylammonium. For wild-type ELIC, the mean (black solid line) ± 1 SD (gray error bars) of responses recorded from eight (short pulses) or nine (long pulses) different whole-cell experiments are displayed. For the mutants, the displayed traces are currents recorded from representative individual cells. The distribution of ions across the membrane was asymmetrical (∼150 mM/5 mM K+, inside/outside). The command potential was zero, and the −1.6-mV liquid-junction potential between the pipette and bath solutions was offset. As a result, the membrane potential was close to zero, thus approximating the conditions used for cryo-EM image acquisition. The black dashed lines denote the zero-current baseline. The mutants S202A and L205A + W206A, both in M1, did not elicit measurable currents despite displaying cell-surface expression levels that were comparable to those of the other three mutants.