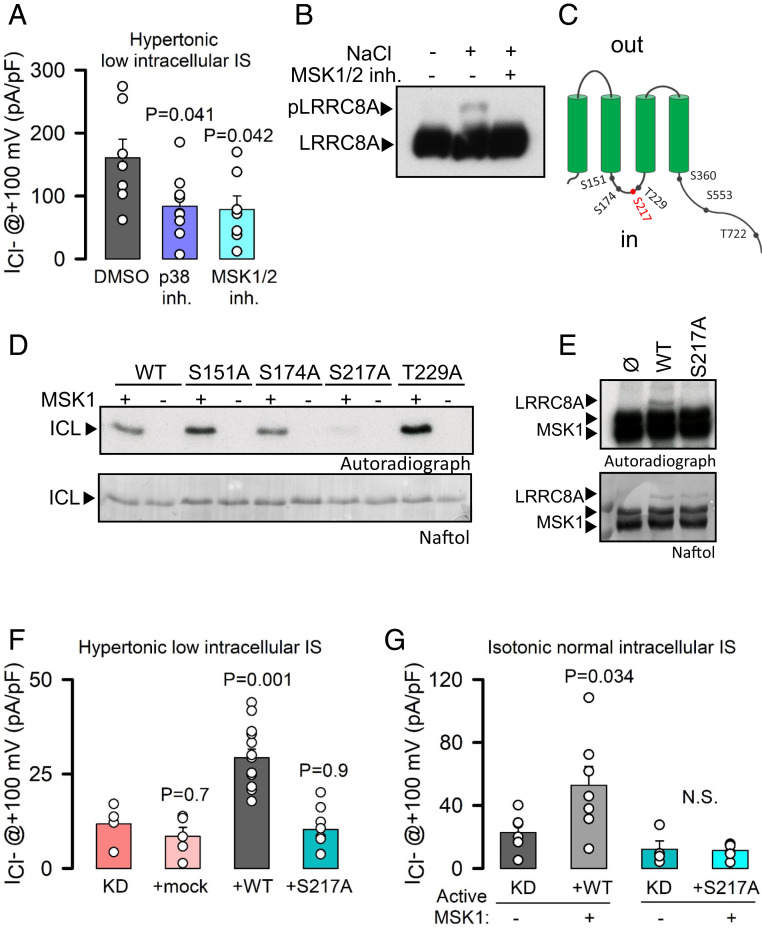
Fig. 2.
The p38/MSK1 pathway regulates LRRC8A activation upon hypertonicity. (A) Maximal mean current densities (±SEM) measured in LZ and KO HeLa cells dialyzed with hyperosmotic solutions of 0.08 IS and exposed to hypertonic solutions containing DMSO (0.1%), the p38 inhibitor (SB203580, 10 μM), or the MSK1 inhibitor (SB747651A, 10 μM). P values were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunnett’s test versus a DMSO control group. (B) Western blot analysis of LRRC8A in a Phos-tag gel of extracts obtained from HeLa cells exposed to hypertonic (+100 mM NaCl) solutions in the absence or presence of SB747651A. (C) Schematic diagram of MSK1 phosphorylation sites in LRRC8A. (D) In vitro phosphorylation by MSK1 of the ICL (amino acids 144 to 258) of LRRC8A-WT as well as of single mutants. (E) In vitro phosphorylation of full-length LRRC8A-WT and LRRC8A-S217A by MSK1. (F) Maximal mean current densities (±SEM) measured in stable LRRC8A KD HeLa cells overexpressing shRNA-resistant LRRC8A-WT or LRRC8A-S217A. Cells were dialyzed with hyperosmotic solutions with an IS of 0.08 and exposed to hypertonic solutions. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunnett’s test versus KD control group. (G) Maximal mean current densities (±SEM) measured in KD HeLa cells recorded under control isotonic conditions. Cells overexpressed shRNA-resistant WT or S217A LRRC8A with or without coexpression of a constitutively active MSK1 (MSK1-T581D/T700D). P values were determined by Student’s t test comparing the effects of MSK1 expression on WT or mutant channel.