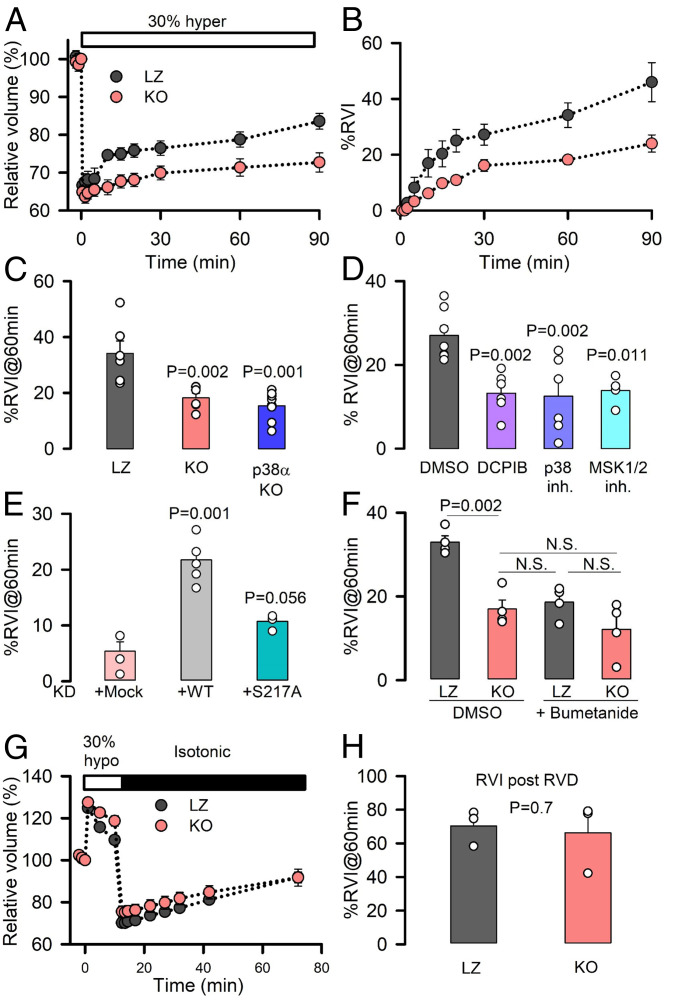
Fig. 3.
The p38/MSK1 pathway and LRRC8A regulate NKCC-mediated RVI. (A) Time course of relative changes in cell volume of LZ and KO HeLa cells (normalized to isotonic conditions) before and after exposure to a 30% hypertonic medium. Mean ± SEM (n = 6). (B) Percentage of RVI, calculated as the percentage of volume recovered following the initial cell shrinkage at the different time points after the hypertonic stress. (C) Mean RVI (%) calculated at 60 min in LZ (n = 6), KO (n = 6), or p38α-KO (n = 9) HeLa cells. (D) Mean RVI (%) calculated at 60 min in HeLa cells superfused with DMSO (n = 7), the LRRC8A channel inhibitor DCPIB (n = 6), the p38 inhibitor SB203580 (n = 6), or the MSK1 inhibitor SB747651A (n = 4). (E) Mean RVI (%) calculated at 60 min in KD (n = 4) HeLa cells overexpressing shRNA-resistant WT (n = 6) or S217A (n = 4) LRRC8A channels. (F) Mean RVI (%) calculated at 60 min after LZ or KO HeLa cells were exposed to DMSO or 50 μM bumetanide. (G) Relative changes in cell volume measured before and after superfusion of LZ or KO HeLa cells with a 30% hypotonic medium. (H) Mean RVI (%), generated after RVD, was calculated at 60 min after return to isotonic medium, as shown in G (n = 3). P values were determined by two-tailed Student’s t test (H), a Bonferroni's all pairwise comparison (F), or one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunnett’s test versus control group (Left Bar) (all others).