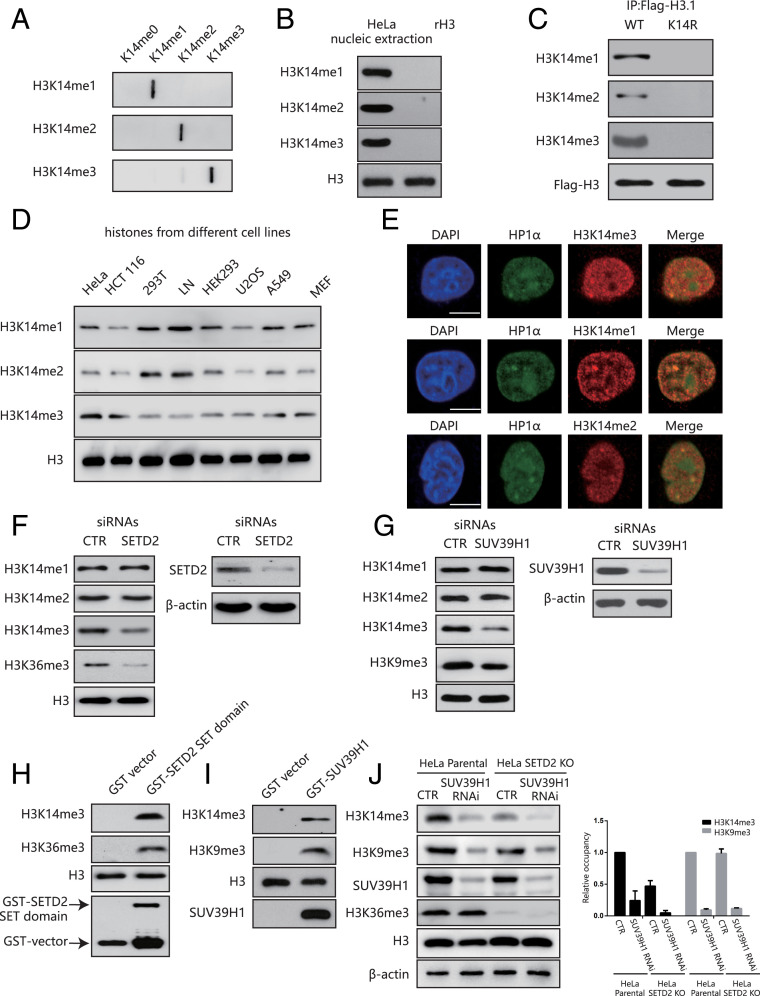
Fig. 1.
H3K14 is methylated in mammals by SETD2 and SUV39H1. (A) A slot-blot assay showing the specificity of the H3K14 methylation antibodies. (B) H3K14 methylation expression in HeLa cells. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with a Flag-H3.1 WT or a Flag-H3.1K14R before anti-Flag immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. (D) The H3K14 methylation expression levels in different cell lines. (E) HeLa cells were labeled with anti-H3K14me1, H3K14me2, H3K14me3 (red), or HP1-α (green) antibodies and analyzed under a confocal microscope. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (F) HeLa cells were transfected with SETD2 siRNAs or a nonspecific siRNA (CTR). The whole-cell lysates and histones were extracted for Western blotting. (G) HeLa cells were transfected with SUV39H1 siRNAs or a nonspecific siRNA (CTR). The whole-cell lysates and histones were extracted for Western blotting. (H) In vitro methylation assay using a recombinant SETD2 SET domain as the enzyme. Free recombinant histone H3 was used as the substrate. (I) In vitro methylation assay using recombinant SUV39H1 as the enzyme. Free recombinant histone H3 was used as the substrate. (J) HeLa parental cells and SETD2-KO HeLa cells were transfected with or without SUV39H1 siRNAs or a nonspecific siRNA (CTR). The whole-cell lysates were extracted for Western blotting (Left). Quantification of the band density (Right). The band density of HeLa parental cells in “CTR” was normalized to 1. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 3).