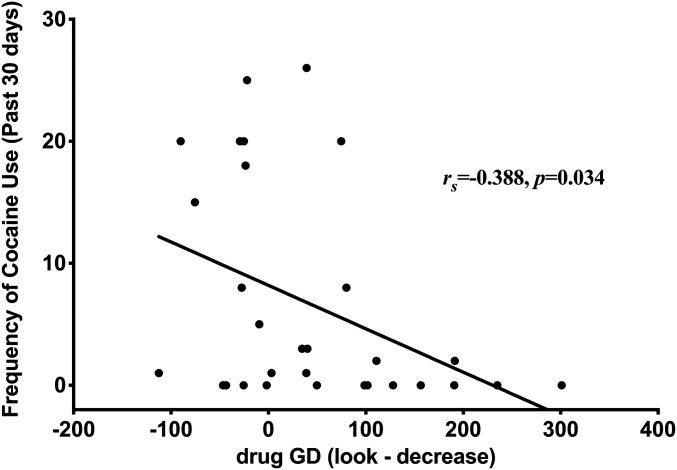
Fig. 5.
The reduction in drug-related GD negatively correlated with the frequency of cocaine use in the past 30 d (rs = −0.388, P = 0.034), such that individuals with cocaine use disorder who used less frequently in that past 30 d demonstrated a greater reduction in GD to drug-related cues in response to the instruction to “Decrease” (versus “Look”) their emotional cue reactivity.