Figure 4. Administration of propranolol decreases fear expression and alters memory traces in the dorsal dentate gyrus of ArcCreERT2 x eYFP mice.
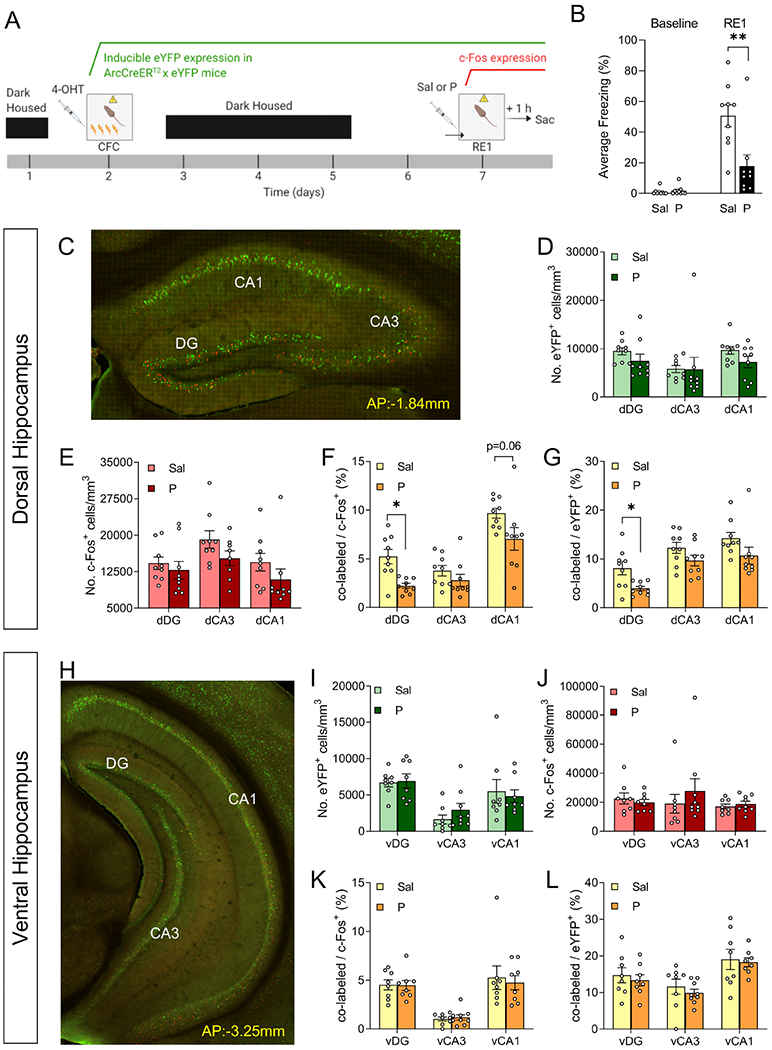
(A) Experimental design. (B) Injection of propranolol prior to the RE1 decreases freezing behavior. (C) Representative image of the dorsal hippocampus. The number of (D) eYFP+ cells or (E) c-Fos+ cells does not differ in dDG, dCA3, or dCA1 following administration of propranolol. The percentage of (F) co-labeled/c-Fos+ cells and (G) co-labeled/eYFP+ cells significantly decrease in the dDG following administration of propranolol, but not in dCA3 or dCA1. (H) Representative image of the ventral hippocampus. The number of (I) eYFP+ cells or (J) c-Fos+ cells does not differ in vDG, vCA1, or vCA3 following administration of propranolol. The percentage of (K) co-labeled/c-Fos+ cells and (L) co-labeled/eYFP+ cells does not differ in dDG, dCA1 or dCA3 following administration of propranolol. (n = 9 male mice per group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Error bars represent ± SEM. eYFP, enhanced yellow fluorescent protein; 4-OHT, 4-hydroxytamoxifen; CFC, contextual fear conditioning; RE1, context re-exposure; sac, sacrifice; Sal, saline; P, propranolol; dDG, dorsal dentate gyrus; dCA1, dorsal CA1; dCA3, dorsal CA3; vDG, ventral dentate gyrus; vCA1, ventral CA1; vCA3, ventral CA3.
