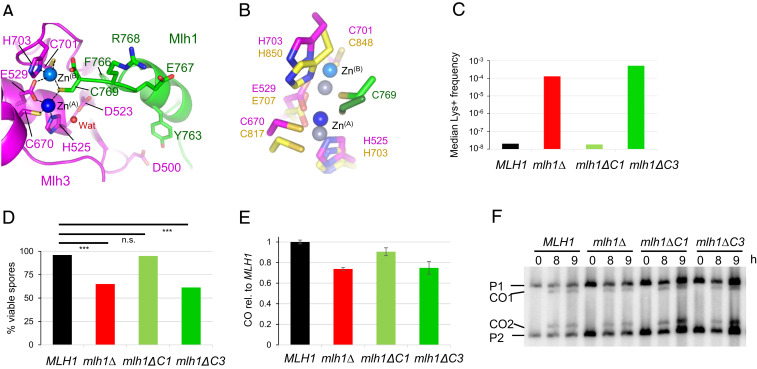
Fig. 2.
Role of the last residues of Mlh1 in the active site of Mlh3 and Pms1. (A) Endonuclease site of MutLγ with two zinc atoms. Mlh1 and Mlh3 are colored respectively in green and magenta. The Zn atom called ZnA is colored in dark blue and the second one, called ZnB, is colored in light blue. Water molecules are colored in red. (B) Superimposition of Pms1 and Mlh3 active sites. ZnA and ZnB in Pms1 are colored in greys. Names of Pms1 residues are in yellow. C769 of Mlh1 in Mlh1-Pms1 complex is in green. (C) Mutation rates measured with a Lys+ reported assay with mlh1 alleles deleted of the last residue (mlh1∆C1) or the last three residues of Mlh1 (mlh1∆C3). The median values from a fluctuation analysis (see Materials and Methods) are plotted. MLH1 and mlh1∆ data were measured in (48). (D) Spore viability of diploid strains bearing the indicated MLH1 genotype at its endogenous locus. ***P < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test. Refer also to SI Appendix, Table S2. (E–F) Crossing over frequency at the HIS4LEU2 hotspot monitored by Southern blot. Graph shows quantification at 8 and 9 h from two independent biological replicates ± range and are expressed relative to levels in MLH1 (same strains as in E).