Fig. 5.
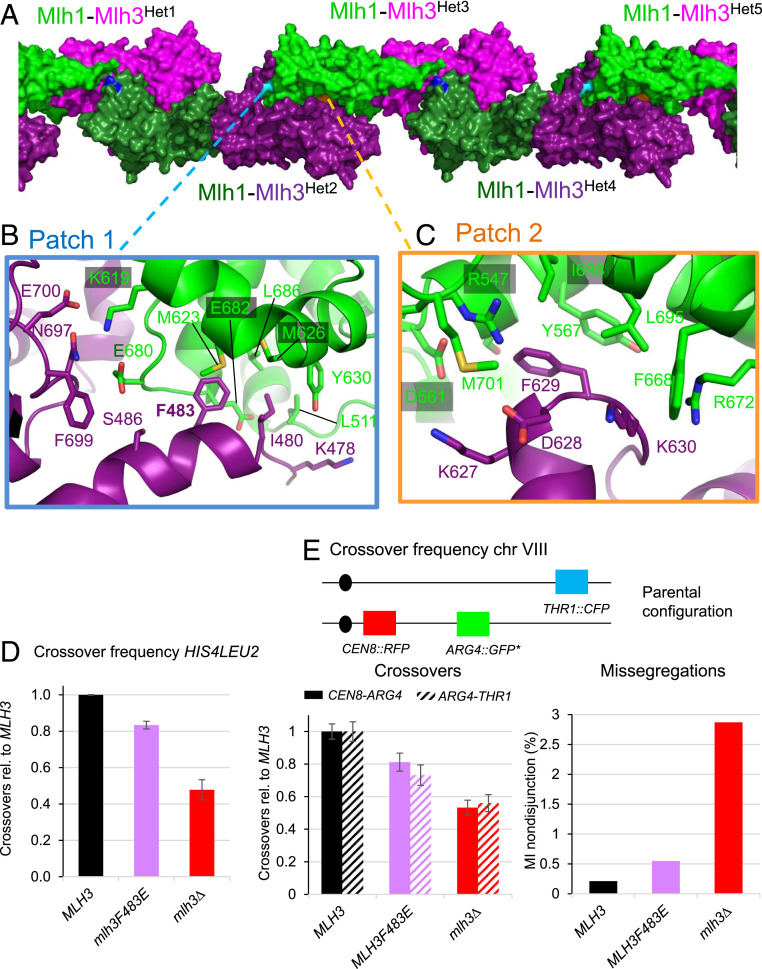
Formation of MutLγ filaments through Mlh3-Cter and Mlh1-Cter interactions. (A) Filament-like structures made by Mlh1-Mlh3 heterodimers in the crystals. The interactions between five heterodimers (Het1 to Het5) in the crystal are represented by alternating the color of the heterodimers with Mlh1-Mlh3 in (green-magenta) or in (dark green-purple). The positions of the three main patches that mediate these structures are shown with the central residues colored respectively in cyan (patch 1), in orange (patch 2), and in blue (patch 3, SI Appendix, Fig. S5A). (B) Patch 1 includes interactions between six Mlh3 residues and nine Mlh1 residues. Most Mlh1 residues belong to the MIP-binding site that is involved in the interaction of Mlh1 with the MIP-motifs observed in Exo1, Ntg2 and Sgs1 (27). The F483 position of Mlh3 is buried in the center of this Mlh1 pocket in a position similar to the aromatic of the MIP motifs of the Mlh1 partners (SI Appendix, Fig. S5 A–C, for the superposition of the MIP motif of Exo1 with the positions of the Mlh3 residues). (C) Patch 2 includes interactions between four Mlh3 residues and eight Mlh1 residues. The Mlh1 side contains the R547 position that interacts in MutLα with a Pms1 C-terminal extension that is not present in Mlh3(CTD). (D) Crossing over frequency at the HIS4LEU2 hotspot monitored by Southern blot. Graph shows quantification at 8 and 9 h from two independent biological replicates ± range and are expressed relative to levels in MLH3. (E) Meiotic crossovers on chromosome VIII. Top: illustration of the fluorescent spore setup (60). Genetic distances are measured in the CEN8-ARG4 and ARG4-THR1 adjacent intervals and expressed relative to the MLH3 values. The MI nondisjunction frequency was measured from the same dataset as for genetic distances, as described previously (60). MLH3: 1898 tetrads; mlh3F483E: 1277 tetrads; and mlh3∆: 1463 tetrads. Error bars: SE.