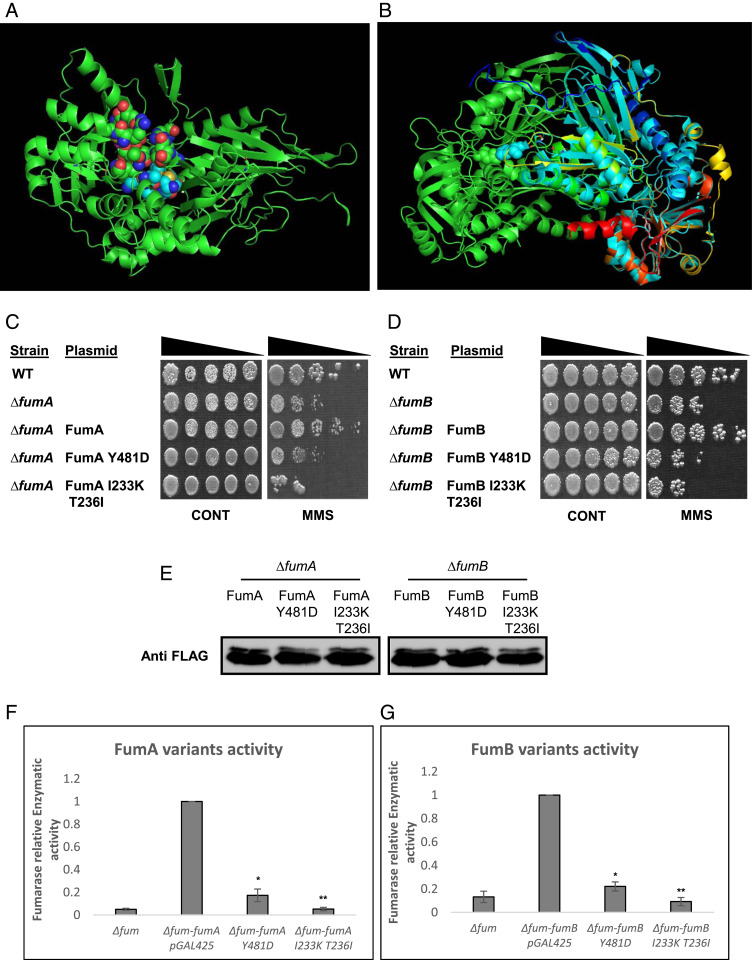
Fig. 3.
FumA and FumB catalytic activity is required for their DNA damage–related function. (A) Model structure as proposed by I-TASSER, catalytic site (homologous to L. major active site) as proposed by PEPTIMAP, and location of important amino acids for the function of this enzyme as proposed by CONSURF. (B) Alignment of proposed FumA/FumB structure with FH of L. major (5l2R). (C) E. coli WT, ΔfumA, and ΔfumA harboring the indicated plasmids and (D) E. coli WT, ΔfumB, and ΔfumB harboring the indicated plasmids were grown to midexponential phase (OD600 nm = 0.3), treated with MMS (0.35% MMS [vol/vol] for 45 min), and subjected to a spot test assay. (E) E. coli ∆fumA and ∆fumB harboring the indicated plasmids were grown to midexponential phase (OD600 nm = 0.3) and treated with MMS (0.35% MMS [vol/vol] for 45 min). The cells were lysed and centrifuged to obtain the supernatants which were subjected to Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (F and G) fum-null mutant (ΔfumACB) harboring the indicated plasmids was grown to exponential phase, and the cells were lysed and centrifuged to obtain the supernatant, which was assayed for fumarase activity at 250 nm with L-malic acid as the substrate (mean ± SD [n = 3], two-tailed Student’s t test *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).