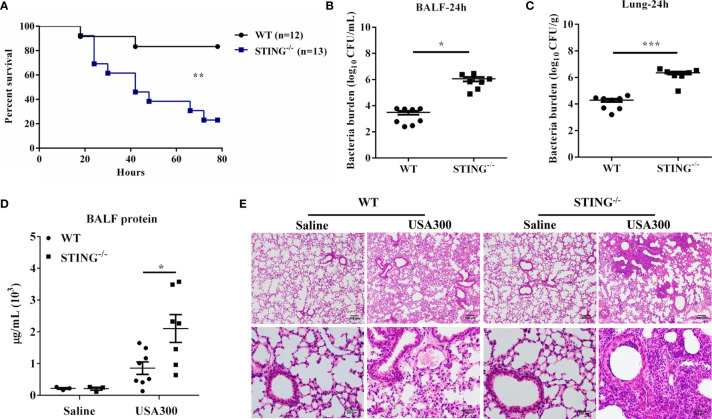
Figure 1.
STING-deficient mice display increased susceptibility to S.aureus pulmonary infection. WT and STING-/- mice were infected intranasally with S.aureus. (A) Survival was monitored up to 80 hpi (2 × 108 CFU, N = 12-13/group). WT and STING-/- mice (N = 7-8/group) were infected intranasally with a sublethal inoculum of S.aureus (1 × 108 CFU/mouse) for 24 h and then euthanized to quantitate the bacterial burden in (B) BALF, (C) lung. (D) Total protein in BALF was measured. (E) Lung tissue structures were observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining (magnification of 100 × or 400 ×). All data are shown as mean ± SEM. Student’s t-test was performed. Log-rank test was used for statistical analysis of animal mortality. Statistical significance is indicated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.