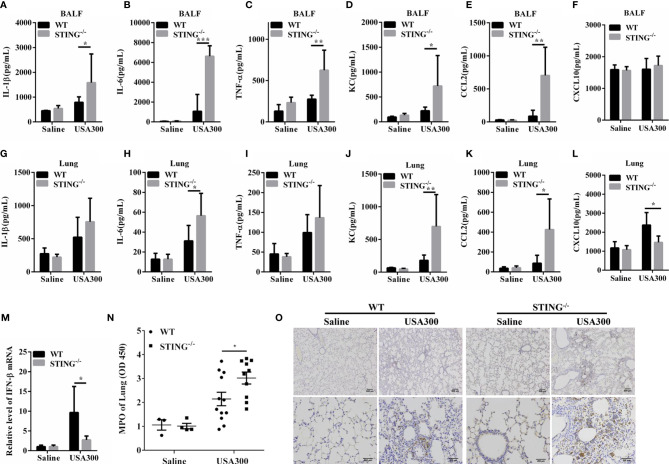
Figure 2.
STING deficiency leads to enhanced pro-inflammatory mediator production following S.aureus lung infection. WT and STING-/- mice (N = 7-8/group) were infected intranasally with S.aureus (1 × 108 CFU/mouse) for 24 h. The homogenate supernatants of lungs and BALF were detected for concentrations of indicated cytokines and chemokines by ELISA. (A, G) IL-1β, (B, H) IL-6, (C, I) TNF-α, (D, J) KC, (E, K) CCL2, (F, L) CXCL10. (M) Lung tissue mRNA was examined for IFN-β by qRT-PCR. (N) The homogenate supernatants of lungs were also used to determine the activity of MPO (a neutrophil marker). (O) Representative immunohistochemical staining of Gr-1 (a neutrophil marker) was performed in the pulmonary sections. All data are shown as mean ± SEM. Student’s t-test was performed. Statistical significance is indicated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.