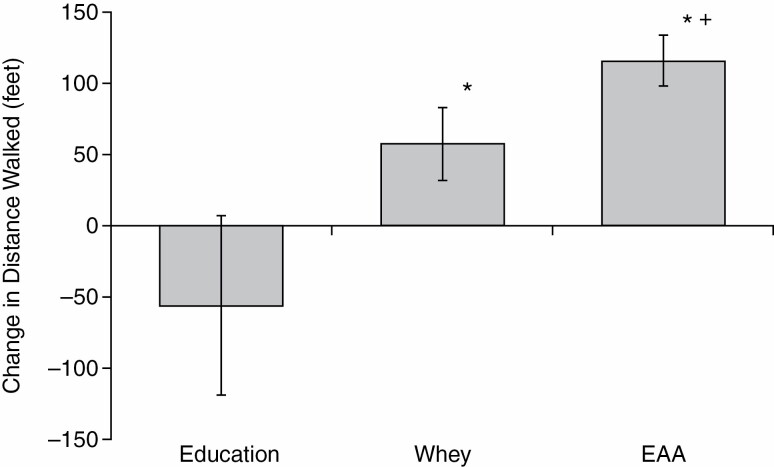
Figure 1.
Change in distance walked in 6 min at 12 wk of intervention as compared to the preintervention value. Values are mean ± SEM. The distance walked was significantly improved (*) in participants who consumed daily supplements of whey protein (n = 32, p = .039) or essential amino acids (EAAs) (n = 28, p < .0001). The improvement in the EAA group was significantly greater than the improvement in the Whey Protein group (+) (p = .029). The reduction below the pre-value in the Education-only group (n = 32) was not statistically significant.