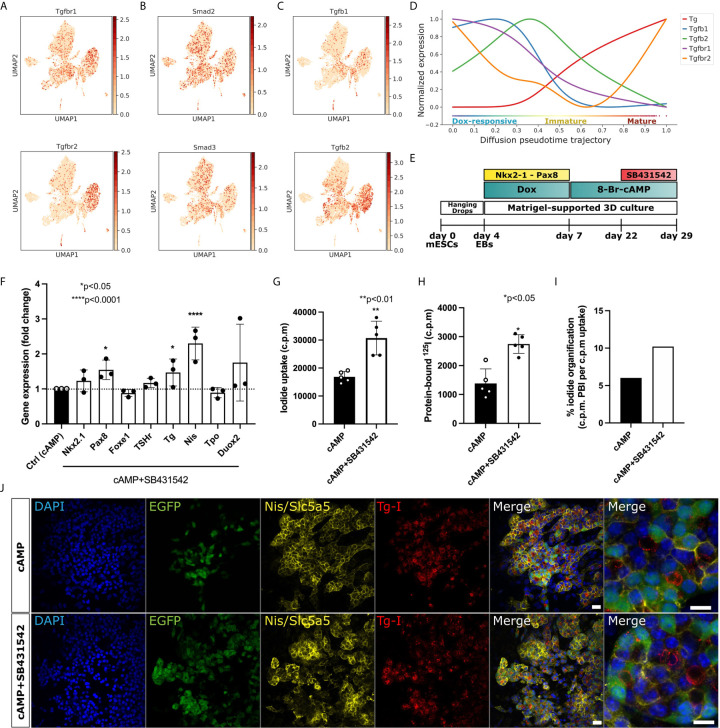
Figure 4.
Enhancement of maturation efficiency by pharmacological inhibition of TGF-beta. (A) UMAPs demonstrate TGF-beta receptors (Tgfbr1 and Tgfbr2), (B) activators (Smad2 and Smad3) and (C) ligands (Tgfb1 and Tgfb2) are expressed in mesoderm cells and in thyroid cluster. (D) Expression trends of TGF-beta receptors and ligands along pseudotime trajectory in thyroid cells. (E) Schematic representing the thyroid differentiation protocol to test the impact of TGF-beta inhibition on thyroid organoid maturation. TGF-beta inhibition was induced by co-treatment with cAMP+SB431542 from day 22 to day 29. (F) qPCR analysis demonstrates significant upregulation in Pax8, Tg and Nis gene expression after 7 days of TGF-beta pathway inhibition. *p<0.05, ****p<0.001 by Mann-Whitney test (G–I) Functional organification assay confirms significant improvement in 125I uptake (G) and protein-bound 125I (H) under SB431542 treatment, which results in a higher percentage of cells with capacity of 125I organification (I). **p< 0.01, *p<0.05 by Student’s t-test. (J) Immunofluorescence staining demonstrating that SB431542 treatment does not affect thyroid follicular organization evidenced by Nis specific expression and Tg-I presence in the lumen space Scale bar: 20 µm and 10 µm (inset).