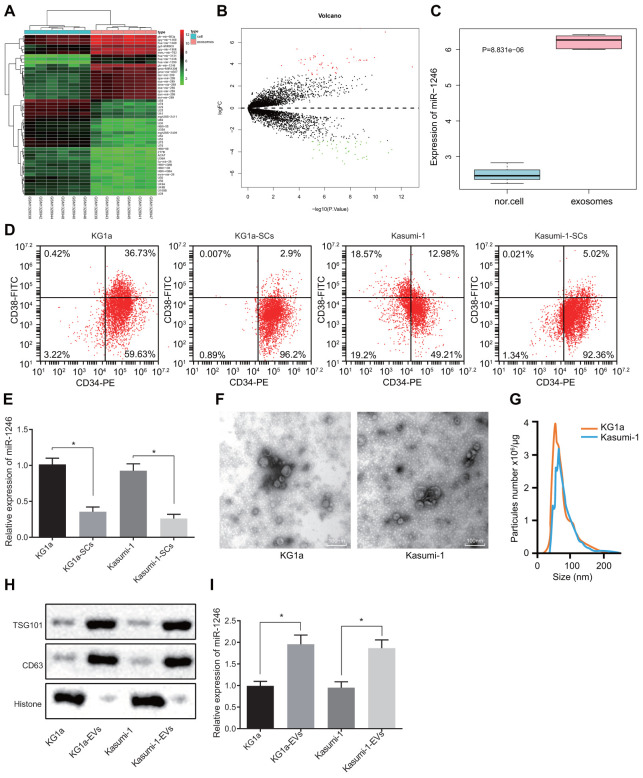
Figure 1.
High levels of miR-1246 expression are identified in AML cell-derived EVs. (A) Heat map of differentially expressed miRNAs from the GSE55025 profile. (B) Volcanic map of differentially expressed miRNAs in GSE55025. (C) Boxplot of miR-1246 in expression profile GSE55025. The left box refers to expression in normal cell-derived EVs, and the right box represents the expression in AML cell-derived EVs. (D) AML cell lines labeled with CD34-PE and CD38-FITC antibodies. The subpopulation of CD34+CD38−cells (i.e., LSCs) was analyzed by flow cytometry. (E) Expression of miR-1246 in AML cell lines (KG1a and Kasumi-1) as well as LSCs detected by RT-qPCR. (F) Morphology of AML cell-derived EVs observed by TEM. (G) EV concentration and particle size measured by nanoparticle tracking analysis. (H) Expression of EV specific markers CD63 and TSG101 assessed by western blot analysis. (I) Expression of miR-1246 in AML cell lines (KG1a and Kasumi-1) and in corresponding EVs as detected by RT-qPCR. * p < 0.05 vs. KG1a or Kasumi-1 cells. Data in the figures are all measurement data, expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Independent sample t-test was applied for comparison between two groups. The experiments were repeated in triplicate.