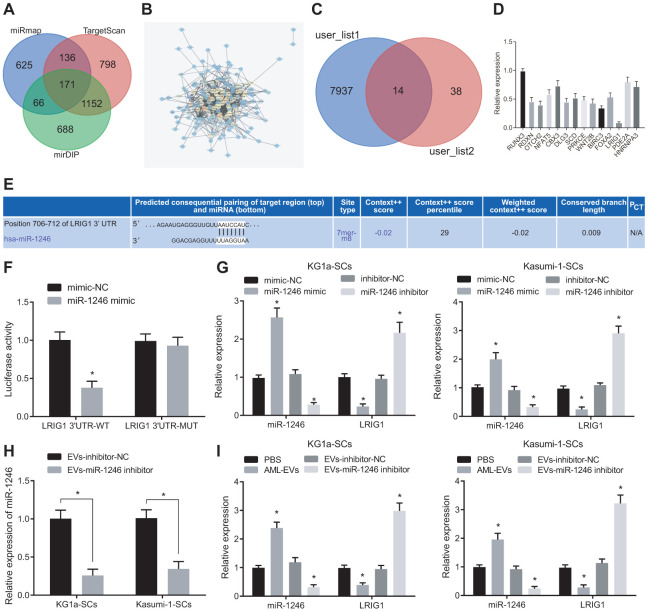
Figure 4.
AML cell-derived EVs containing miR-1246 target LRIG1 in LSCs. (A) Venn diagram of target gene retrieved from databases of mirDIP, TargetscanHuma and miRmap. (B) PPI analysis of 171 intersected target genes. (C) Venn diagram of 52 genes with junction points ≥ 10 in PPI analysis and low-expressed genes in leukemia from the TCGA database. (D) Quantitative analysis of 14 screened genes. (E) The binding site of miR-1246 to LRIG1 according to the Targetscan Huma database. (F) The binding relationship between miR-1246 and LRIG1 was verified by dual luciferase reporter gene assay. (G) miR-1246 and LRIG1 expression in LSCs after transfection with miR-1246 mimic or miR-1246 inhibitor assessed by RT-qPCR. (H) Expression of miR-1246 in AML cell secreted EVs with miR-1246 inhibition measured by RT-qPCR. (I) Expression of miR-1246 and LRIG1 in LSCs after co-culture with AML cell-derived EVs detected by RT-qPCR. * p < 0.05 vs. LSCs co-cultured with PBS or EVs-inhibitor-NC. Data in the figures are all measurement data, expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Independent sample t-test was applied for comparison between two groups. Data among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. The experiments were repeated in triplicate.