Fig. 4. NMDA receptor dependent Mg2+ influx and p38 MAPK activation in delayed pCREB by NMDA in primary neurons.
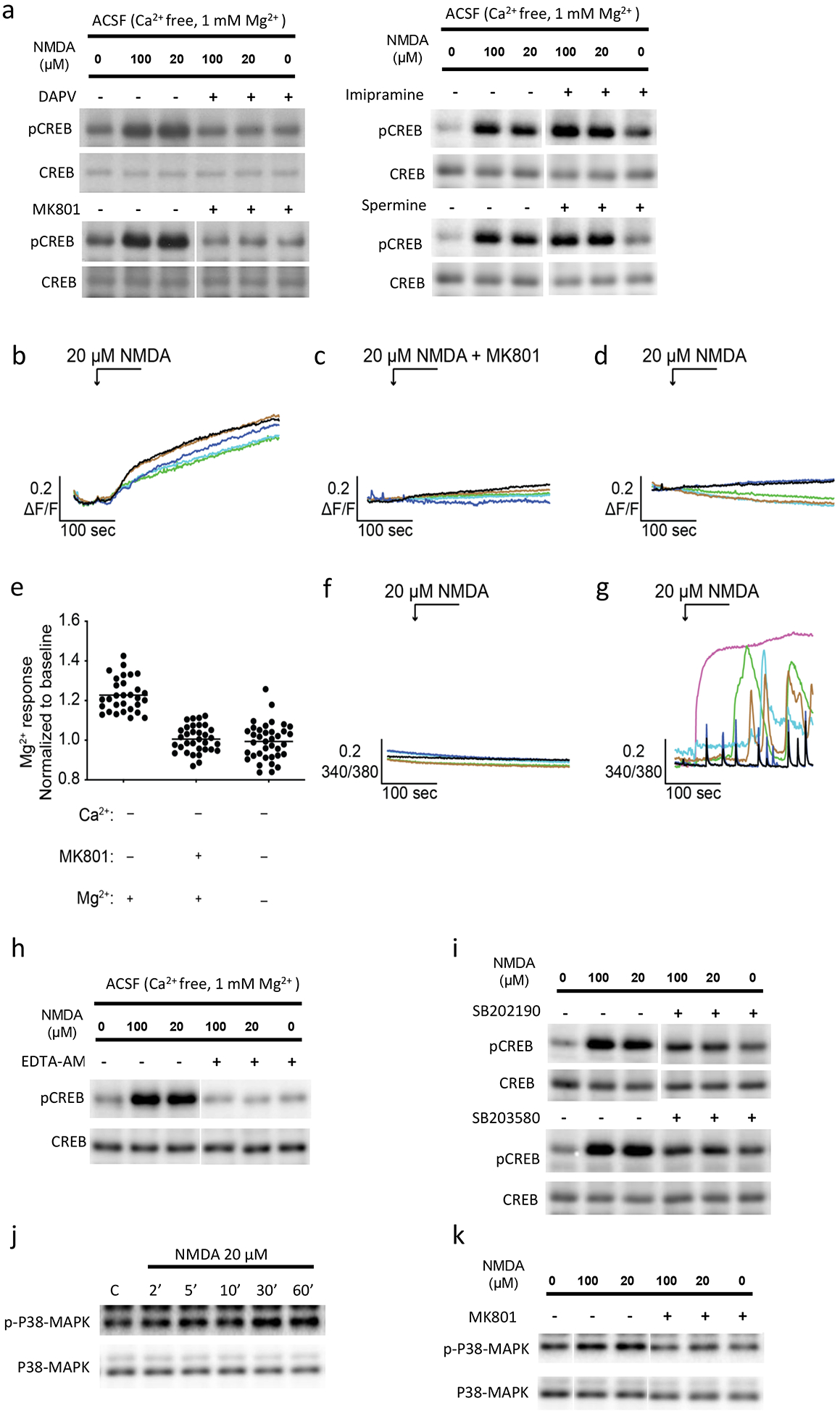
a: D-APV and MK801, but not imipramine and spermine, blocked the delayed pCREB by NMDA at 10 minute time point. D-APV, competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, 50 μM; MK801, NMDA receptor open channel blocker, 10 μM; impramine, Na+-Mg2+ exchanger inhibitor, 100 μM; or spermine, TRPM2 and TRPM7 channel blocker, 10 μM, was included in calcium free ACSF incubation with neurons for 1 hour before NMDA application. b: Primary neurons were loaded with 4 μM of Magnesium Green AM in normal ACSF for 20 min. Cells were then perfused with Ca2+ free ACSF, followed by the stimulation of 20 μM NMDA. This resulted in a gradual increase in the concentration of the intracellular Mg2+. This increase was blocked by either preincubation with 50 μM MK801 for 2 min (c, e) or by removing the extracellular Mg2+ (Ca2+ free ACSF) (d, e). Further, cells were loaded with 2 μM intracellular Ca2+ indicator, Fura-2 AM, for 20 min, followed by the stimulation of 20 μM NMDA in ACSF. Intracellular Ca2+ signals were not changed after NMDA stimulation in Ca2+ free ACSF (with 2 mM EGTA)(f). Robust Ca2+ responses were observed in the presence of extracellular Ca2+ (normal ACSF) (g). (*, P<0.05). h: EDTA-AM (200 μM) incubation with neurons abolished the effect of Mg2+ on delayed pCREB by NMDA. i. p38 MAPK inhibitor SB202190 or SB203580 blocked the effect of delayed pCREB by NMDA in calcium free ACSF. j. Time-course of p38 MAPK phosphorylation in neurons in Ca2+ free ACSF. k. Pre-treatment of MK801 (10 μM) blocked NMDA induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation in Ca2+ free ACSF.
