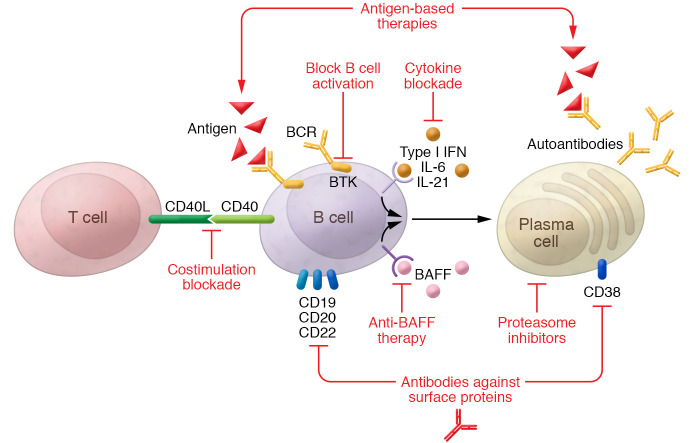
Figure 1. Different strategies to interfere with B cell proinflammatory function in patients with SLE.
Strategies include B cell and plasma cell depletion (e.g., antibodies directed at surface proteins or proteasome inhibitors), selective depletion of autoreactive B cells (e.g., BAFF inhibition), antigen-based therapies that block pathogenic antibodies, and prevention of B cell activation (e.g., blockade of B-T cell costimulation or B cell–activating cytokines).