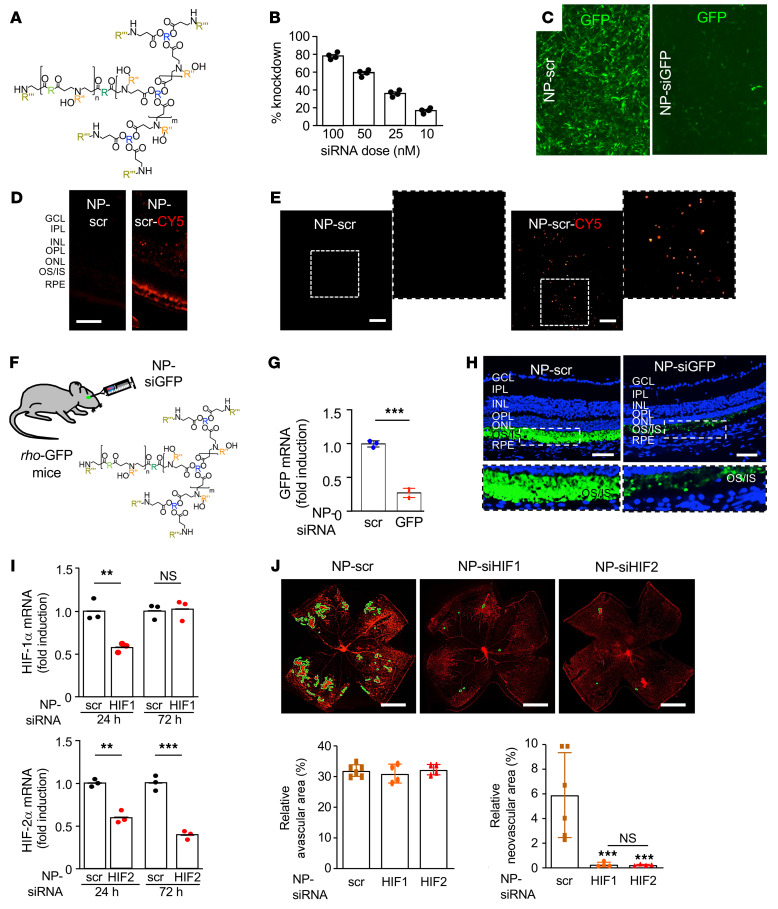
Figure 12. In vivo nanoparticle-mediated RNAi targeting either HIF-1α or HIF-2α prevents the development of retinal NV in OIR mice.
(A) rBEAQ polymer for in vivo delivery of RNAi. (B) rBEAQ polymer nanoparticle-mediated knockdown of GFP reporter gene in NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing GFP in vitro. (C) Fluorescence micrograph of NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing GFP treated with rBEAQ nanoparticles encapsulating a nontargeting scrambled control siRNA (NP-scr) or with nanoparticles encapsulating siRNA targeting GFP (NP-siGFP). Images were taken 1 day after transfection and show sequence-specific GFP knockdown. (D and E) Expression of fluorophore in retinal cross-section (D) and flat mount (E) of mice 1 day after intravitreal injection with NP-scr or NP-scr conjugated to Cy5. (F) Schematic demonstrating use of NP-siGFP to knock down expression of GFP in photoreceptors in rho-GFP mice. (G and H) Expression of GFP mRNA (G) and protein (H) in rho-GFP mice 3 days after intravitreal injection with NP-siGFP versus NP-scr. (I) Hif1a and Hif2a mRNA expression 1 and 3 days after a single intravitreal injection with RNAi targeting HIF-1α or HIF-2α (NP-siHIF1 or NP-siHIF2), respectively. (J) Retinal NV (outlined) at P17 after inhibition of HIF-1α or HIF-2α expression with a single intravitreal injection with NP-siHIF1 or NP-siHIF2, respectively (above). Quantitation of avascular retina and retinal NV at P17 (below) after inhibition of HIF-1α or HIF-2α expression with a single intravitreal injection with NP-siHIF1 or NP-siHIF2 compared with NP-scr. Data are shown as mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed by 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison test (I) or 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison test (J). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. n = 4–6 animals. GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; IS/OS, inner/outer segments; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; h, hours; NS, nonsignificant. Scale bar: 100 μm (D, E, and H); 500 μm (J).