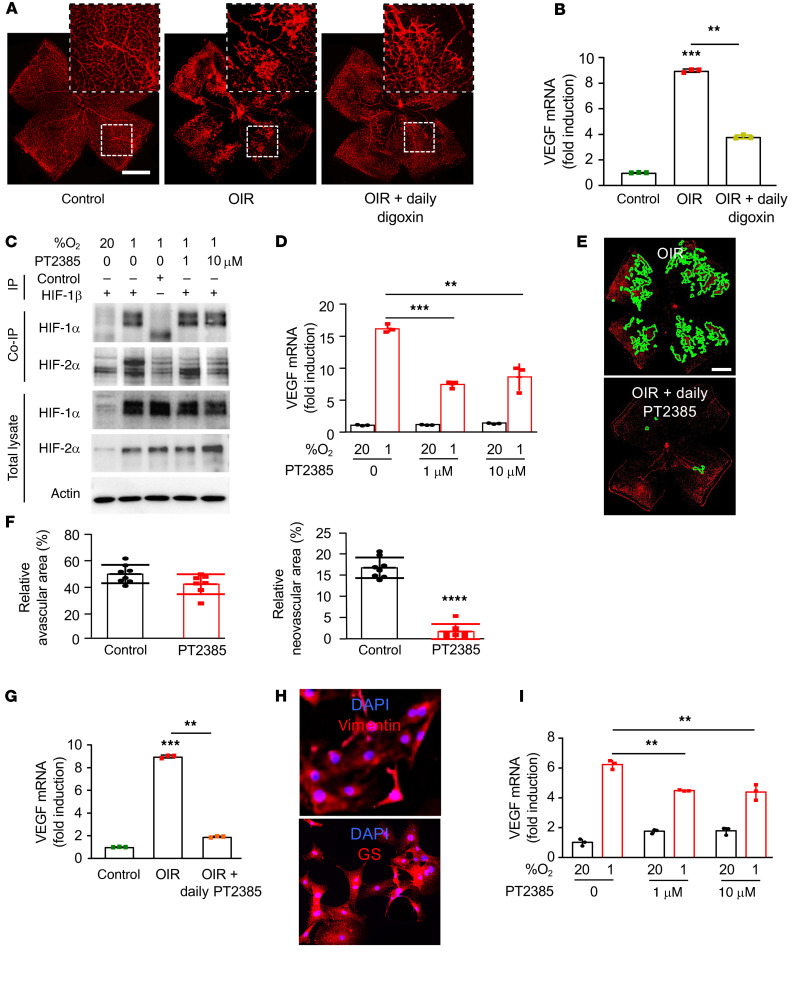
Figure 8. Inhibition of HIF-2α modestly affects VEGF expression in vitro but markedly reduces retinal NV in vivo.
(A) Representative retina flat mounts demonstrating the promotion of retinal NV at P17 in the OIR mouse model after daily i.p. injection (P12–P16) with the HIF-1 and HIF-2 inhibitor digoxin (0.5 mg/kg). (B) Expression of VEGF mRNA expression in MIO-M1 cells treated with increasing doses of PT2385 for 24 hours. (C) Binding of endogenous HIF-1β to HIF-1α or HIF-2α in MIO-M1 cells treated with the HIF-2–specific inhibitor PT2385 (at the specified doses) or vehicle (DMSO) and exposed to 20% or 1% O2 for 24 hours was detected by co-IP. (D) Expression of Vegf mRNA expression in retina from OIR mice after daily i.p. injection (P12–P16) with digoxin. (E) Representative retina flat mounts demonstrating the inhibition of retinal NV at P17 in the OIR mouse model after daily oral gavage (P13–P16) with PT2385 (30 mg/Kg) or vehicle. (F) Quantitation of retinal avascular area (left) and retinal NV (right) at P17. (G) Expression of Vegf mRNA expression in retina from OIR mice after daily oral gavage (P12–P16) with PT2385. (H) IF of primary retinal Müller cells isolated from mice demonstrating expression of key Müller cell markers, vimentin (above) and GS (below). (I) Expression of Vegf mRNA expression in primary mouse Müller cells treated with PT2385 (at the specified doses) for 16 hours. Data are shown as mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed by 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison test (B and G), 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison test (D and I), or 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (F). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Scale bars: 500 μm (A and E).