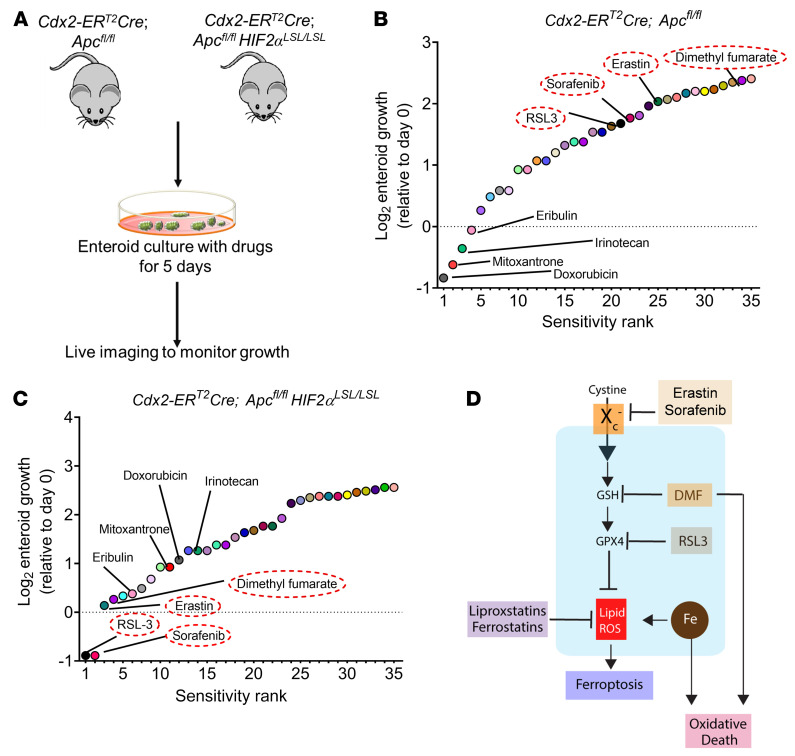
Figure 1. Screening of compounds that exhibit reduction in growth of HIF-2α–overexpressing tumor enteroids.
(A) Schematic of enteroids isolated from a sporadic CRC mouse model (Cdx2-ERT2Cre; Apcfl/fl) and CRC HIF-2α–overexpressing mouse model (Cdx2-ERT2Cre; Apcfl/flHIF2αLSL/LSL). (B and C) The log2 fold change in AUC from cell viability dose-response curves for each compound in the library, signifying the most sensitive (sensitivity rank 1) to least sensitive (sensitivity rank 35) compounds (n = 10). (D) Schematic of known oxidative cell death pathways of the 4 most significant compounds from the screen, indicating ferroptosis activators, such as erastin, RSL3, and sorafenib, that inhibit Slc7a11 or GPX4 and induce lipid peroxides. The process of lipid ROS (Li-ROS) accumulation can be inhibited by ferroptosis inhibitors, such as ferrostatins and liproxstatins, which directly eliminate lipid peroxide formation. Small molecules such as DMF are known to mediate oxidative stress and cell death by depletion of GSH.