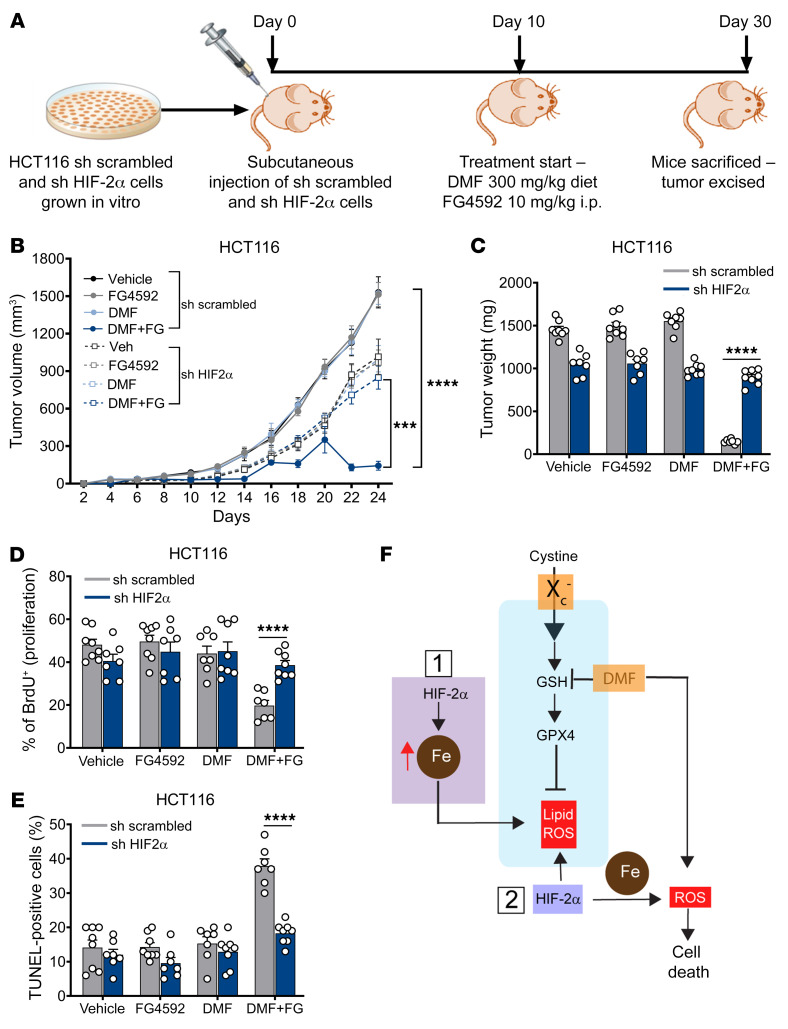
Figure 8. DMF-mediated CRC cell death in vivo is HIF-2α dependent.
(A) Schematic of HIF-2α knockdown xenograft in vivo study. shRNA-mediated HIF-2α knockdown and non–target scrambled HCT116 cells were injected subcutaneously into both flanks of C57BL/6 mice (n = 8 for each group). After visible formation of tumor at day 10, the mice were subjected to the DMF diet (300 mg/kg of chow) and FG4592 (10 mg/kg of mouse body weight). (B) Tumor volume, (C) tumor weight, (D) tumor proliferation, and (E) tumor apoptosis in HIF-2α knockdown and non–target scrambled HCT116 xenograft mice. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (differences between scrambled and HIF-2α knockdown cells for DMF+FG treatment). Unpaired t test was used for calculating statistical significance. (F) Schematic outlining the role of HIF-2α mediating vulnerability to oxidative cell death. HIF-2α mediated iron toxicity and accumulation of lipid ROS, which synergized with ferroptotic activators to enhance CRC cell death. HIF-2α also increased cellular iron and synergize with cellular oxidants such as DMF to enhance irreversible cysteine oxidation and cell death.