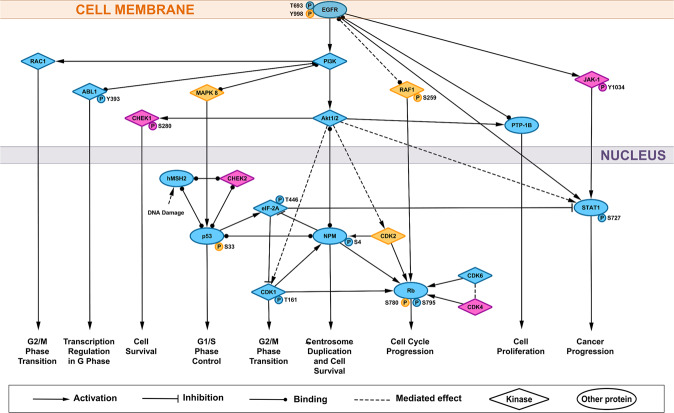
Fig. 1. Representation of the signaling pathways involved in B-cell clonogenicity induced by clonogenic vp17s.
Stimulation of B cells with NHL-a101 and NHL-a102 vp17s induces the activation of several signaling molecules involved in promoting cell survival, cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, G1/S and G2/M phase transition. STRING database and literature data mining were used to identify known and experimentally verified interactions. The several kinases involved in the pathway are represented by diamonds, the other proteins by ellipses. The proteins represented in cyan are the ones activated by both NHL-a101 and NHL-a102. The molecules activated by NHL-a101 are in magenta, the ones stimulated by NHL-a102 in yellow. PI3K: phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; Akt: protein kinase B; CDK1: cyclin-dependent kinase 1; ABL1: tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1; CDK2: cyclin-dependent kinase 2; CDK4: cyclin-dependent kinase 4; CDK6: cyclin-dependent kinase 6; CHEK1: serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1; CHEK2: serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk2; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; eIF-2A: interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase; hMSH2: DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2; JAK-1: tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1; MAPK 8: mitogen-activated protein kinase 8; NPM: nucleophosmin; p53: cellular tumor antigen p53; PTP-1B: tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1; RAC1: ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; RAF1: tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1; Rb: Retinoblastoma-associated protein; STAT1: signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-alpha/beta.