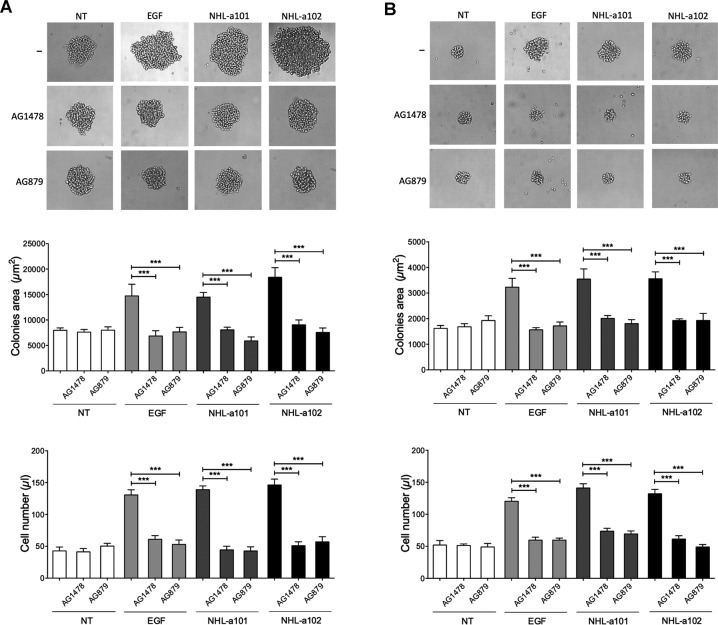
Fig. 3. Effect of EGFR and ErbB2 inhibitors on clonogenic activity of vp17s in B-cells.
A, B Raji (A) and Bjab (B) cells were cultured for 8 days and 12 days, respectively, in the presence or absence of EGF (100 ng/ml) or NHL-a101 or NHL-a102 (10 ng/ml) and EGFR inhibitor AG1478 (250 nM) or ErbB2 inhibitor AG879 (2 μM). Bright-field images represent the characteristic morphology of 2D colonies of Raji and Bjab (upper panels), one colony for each condition is shown (original magnification, ×40). The colony area was measured (15 colonies/condition) by using Leica Qwin image analysis software (central panel). The same number of colonies (15 colonies/condition) was aseptically harvested from 96-well plates and stained with propidium iodide (PI) to detect PI-viable cells by flow cytometry (lower panel). Absolute cell counts were obtained by the counting function of the MACSQuant® Analyzer. Bars represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. The statistical significance between control and treated cultures was calculated using one-way ANOVA and the Bonferroni’s post-test was used to compare data. NT, not treated. ***P < 0.001.