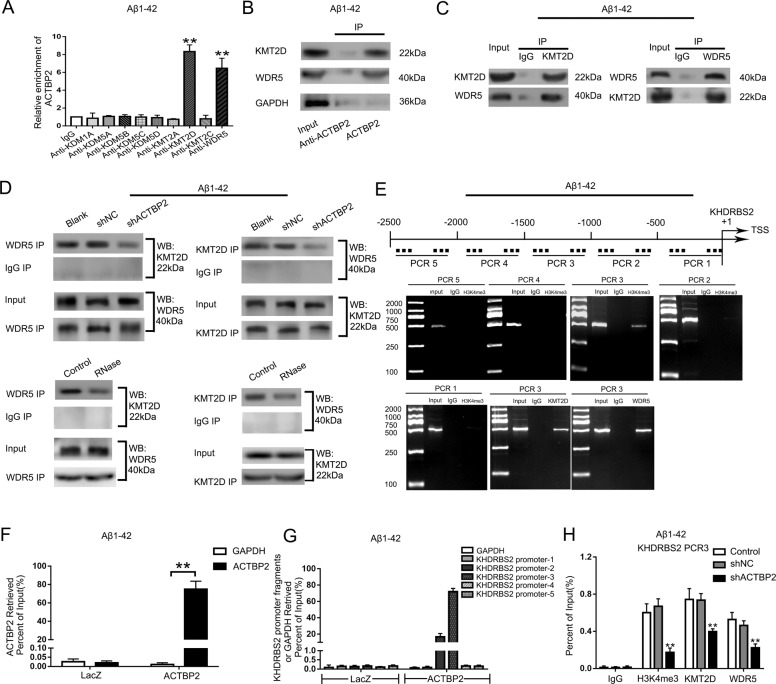
Fig. 3. ACTBP2 interacts with KMT2D and WDR5 methyltransferase modification complex in the KHDRBS2 promoter region in Aβ1–42-incubated ECs.
A RNA immunoprecipitation experiments were performed using specific antibodies. Relative enrichment was measured by qRT-PCR. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). **P < 0.01 versus anti-IgG group. B Western blot of the proteins from antisense ACTBP2 and ACTBP2 pull-down assays. C Co-immunoprecipitation detected the interaction of KMT2D and WDR5 in Aβ1–42-incubated ECs. The specific immunoprecipitation of WDR5 and KMT2D was confirmed by western blot. D Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed to detect the interaction between KMT2D and WDR5 after ACTBP2 knockdown (top) or RNase treatment (bottom). E KHDRBS2 DNA fragments were detected in the chromatin sample immunoprecipitated from Aβ1–42-incubated ECs using the antibody against H3K4me3, KMT2D, or WDR5. F, G ChIRP analysis of ACTBP2 binding to the KHDRBS2 promoters is shown. F The fold enrichment of ACTBP2 in ACTBP2 ChIRP analysis with DNA antisense oligos (asDNA) specific for ACTBP2; G the fold enrichment of KHDRBS2 promoter fragments in ACTBP2 ChIRP analysis. LacZ RNA used as the mock control. (n = 3) H H3K4me3, KMT2D, and WDR5 levels in KHDRBS2 promoter region from 1500 to 1000 bp upstream of the transcription start site (TSS) were decreased after ACTBP2 knockdown in Aβ1–42-incubated ECs. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). **P < 0.01 versus shNC group.