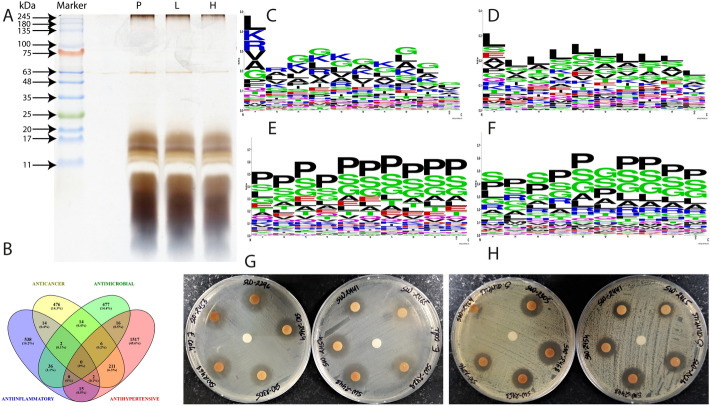
Figure 3.
(A) After subjecting <10 kDa cow urine fraction to Solid Phase extraction, the eluate was collected in 60% ACN, 0.1% TFA. Ethyl acetate extraction of the eluate was carried out and the aqueous phase was separated and dried in Speed Vac. Aqueous extract pooled from different physiological states viz. Heifer, Lactation, and Pregnant (left to right) of Sahiwal cattle were then visualized by tricine-SDS PAGE. (B) Venn diagram showing the number of common peptide sequences shared by different classes of predicted bioactivity. (C) N terminal (10 amino acids) sequence logos were generated for the sequences predicted with certain bioactivity. Antimicrobial Peptide sequences showed glycine, lysine, and leucine as dominant residues. (D) Sequence logo for predicted Anti-Inflammatory sequences, every position is predominated by leucine residue. (E) Sequence logo for predicted Antihypertensive sequences with Proline as dominant residue. (F) Sequence logo for predicted Anticancer sequences with Proline as dominant residue. Both antihypertensive and anticancer sequences show proline as the dominant amino acid at almost every position. (G) 20 µL of Solid Phase Extract eluate from 10 individual animals (Heifer) was coated on 6mm sterile disc and placed on Staphylococcus aureus lawn (equivalent to 0.5 McFarland units). Zone of Inhibition was observed after 12–18 h of incubation. Disc in the center is a negative control containing 20 µL of BSA digest. (H) Peptide extracts activity against Escherichia coli (equivalent to 0.5 Mc Farland). Disc in the center is a negative control containing 20 µL of BSA digest.