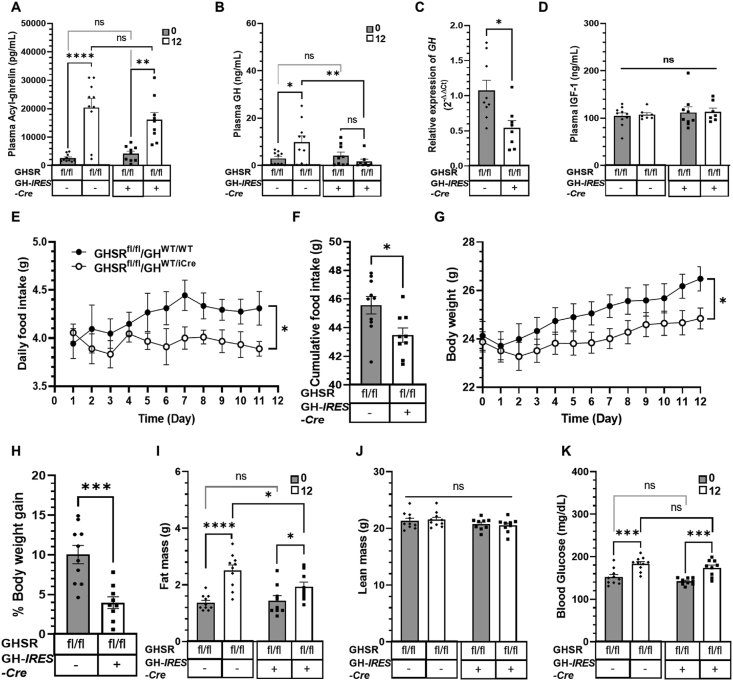
Figure 4.
Effects of somatotroph-selective GHSR deletion and chronic acyl-ghrelin administration on GH secretion, GH mRNA levels, plasma IGF-1, food intake, body weight, and body composition. (A) Plasma acyl-ghrelin and (B) plasma GH measured before (indicated as “0”) and after 12 days (indicated as “12”) of chronic s.c. acyl-ghrelin infusion via osmotic minipumps. (C) Pituitary GH mRNA levels after 12 days of chronic s.c. acyl-ghrelin infusion. (D) Plasma IGF-1 levels before and after 12 days of chronic s.c. acyl-ghrelin infusion. (E) Daily food intake, (F) cumulative food intake, (G) body weight, and (H) % body weight gain over the 12-day course of ghrelin administration. (I) Fat mass, (J) lean mass, and (K) blood glucose measured on the last day of ghrelin administration. Data in A, B, D, E, G, and I–K were analyzed by repeated-measures two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak's multiple comparisons test. Data in C, F, and H were measured by unpaired Student t-test. n = 9–10 (for A-B and E-K), n = 8–9 (for C), n = 7–9 (for D). All the values are expressed as mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.005, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 for statistically significant changes or ns = no significant changes. fl/fl, mice homozygous for the loxP-flanked GHSR gene; –, absence or +, presence of GH-IRES-Cre.