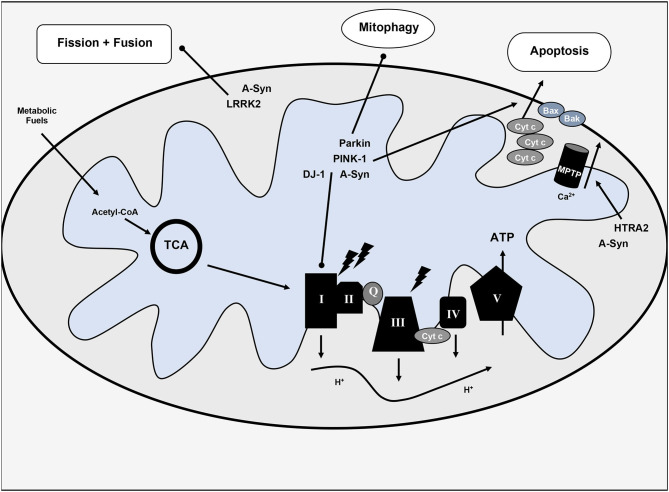
Figure 1.
Overview of mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Various hereditary forms of Parkinson's disease with implicated genes are included with their pathophysiologic mechanisms. TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle or citric acid cycle; Cyt c, cytochrome c; Q, coenzyme Q; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; I-V, complexes I-V of the electron transport chain; MPTP, mitochondrial permeability transition pore; H+, protons; Ca2+, calcium, lighting bolt signifies oxidative stress.