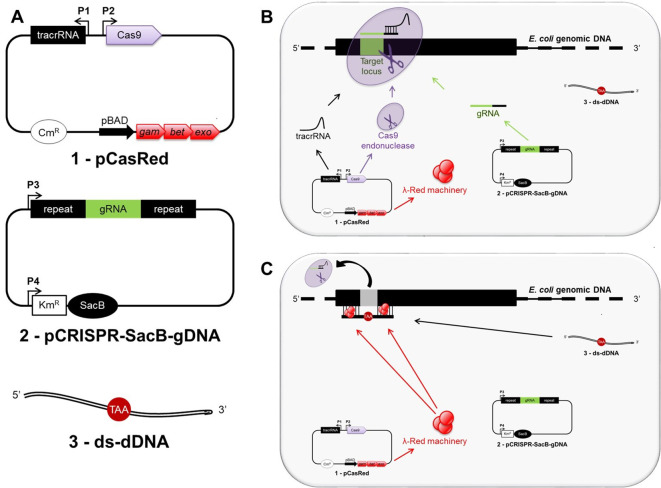
Figure 1. Overview of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing strategy in Escherichia coli.
A shows all three main components required for genome editing in E. coli: 1) the pCasRed plasmid expressing the λ Red (Exo, Beta, Gam) machinery, the Cas9 endonuclease, and the tracrRNA; 2) the pCRISPR-SacB-gDNA plasmid encoding the gRNA and the SacB gene; 3) a synthetic, double-stranded mutagenic oligonucleotide (ds-dDNA). After transformation, the tracrRNA anneals to the gRNA, which specifies the site of cleavage for Cas9 resulting in a three-component complex at the target locus, where the endonuclease activity mediates a chromosomal DNA double strand break (B). The double strand break is subsequently repaired by λ Red-mediated homologous recombination taking place between the extremities of the cleaved chromosomal DNA and the ds-dDNA (C).