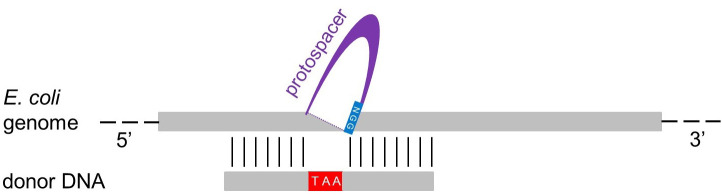
Figure 4. Design of the dDNA.
The donor DNA (dDNA) can vary in length (e.g., 70 or 120 nucleotides, see text). To delete the protospacer + PAM region identified for Cas9 cleavage (Figure 3), the 5’ moiety of the dDNA (35 or 60 nucleotides) has to be complementary to the sequence upstream of the protospacer region, while the 3’ moiety of the dDNA (35 or 60 nucleotides) has to be complementary to the sequence downstream of the protospacer. To inactivate the transcript, an in-frame stop codon (TAA) is inserted, and the PAM region (NGG) is also eliminated to prevent further cleavage through Cas9. Finally, a reverse complement oligonucleotide is designed to get a double-stranded dDNA.