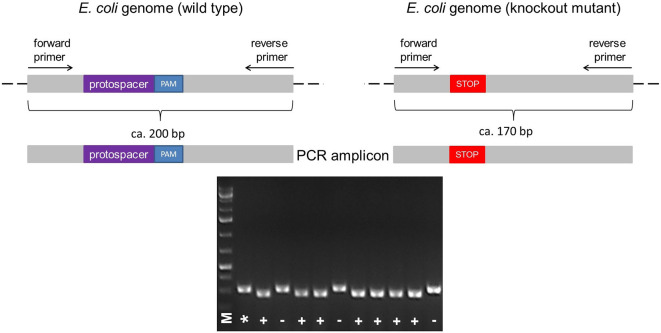
Figure 5. Illustration of the colony PCR.
The forward and reverse primers for PCR are designed to anneal upstream and downstream of the protospacer + PAM sequence, respectively, resulting in the amplification of a ~200 bp fragment in the wild type. According to the size of deletion (e.g., Δ30), a knockout mutant can be identified by its shorter PCR fragment (e.g., ~170 bp) compared to the wild type (A). The PCR fragments different in size can be identified by running a 2% agarose gel electrophoresis (B). Legend: marker (M), wild type control (*), mutant (+), wild type ‘escaper’ (-).