Figure 7.
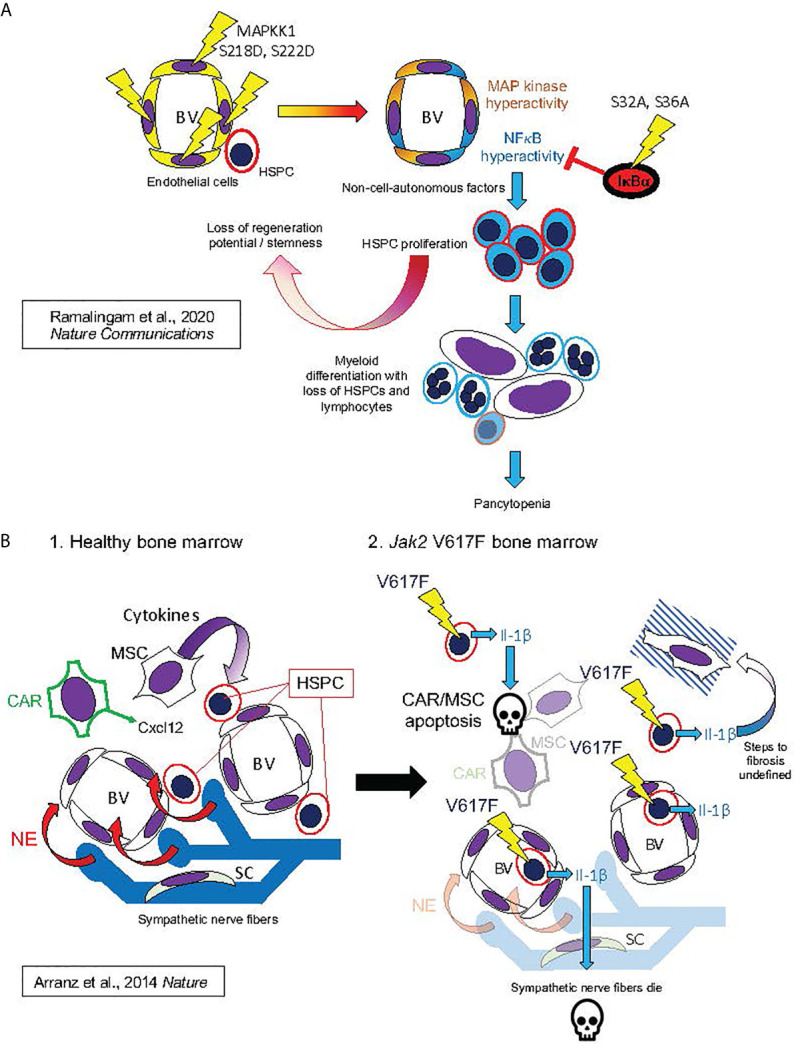
Hypothesized mechanisms of bone marrow niche remodeling in MPNs based on studies in mouse models. This figure illustrates mechanisms hypothesized from mouse model studies by Ramalingam et al. (127) Nature Communications (127) (A) and by Arranz et al. (128) Nature (128) (B). (A) (from top left, following arrows indicating course of pathogenesis): Expression of MAPKK1 S218D, S22D mutant in endothelial cells, resulting in constitutive activation of MAP kinase signaling, also produced constitutive NFκB activation, possibly by a cell-autonomous mechanism, as described in Figure 4A . This led to HSPC proliferation and losses of stemness and regeneration potential in mouse HSPC: phenotypes derived non-cell-autonomously, since mutant MAPKK1 expression was confined to endothelial cells. HSPC phenotypes were dependent on NFκB hyperactivation in HSPC, as they could be entirely rescued by hematopoietic expression of the non-degradable IκBα S32A, S36A “super repressor” mutant. NFκB hyperactivation in HSPC promoted myeloid differentiation with loss of HSPCs and lymphocytes, resulting in pancytopenia and bone marrow failure (a phenotype also observed to result from pan-hematopoietic NFκB hyperactivation in mice) (129–133). (B) Bone marrow remodeling by hematopoietic Jak2 V617F, analogous to human MPNs. 1. In healthy mouse bone marrow, Cxcl12 secreted by CAR cells and cytokines secreted by MSCs maintain HSPCs in the perivascular niche (analogous to Figure 6B ). Bone marrow also contains sympathetic nerve fibers, which secrete norepinephrine (NE). Schwann cells (SC) are associated with the sympathetic neuronal fibers, and essential for their survival. 2. Jak2 V617F, expressed in hematopoietic cells, causes secretion of Il-1β (Il-1α was not assayed). Il-1β caused apoptosis of CAR cells, other MSCs, and Schwann cells, leading to sympathetic denervation of bone marrow. The exact downstream signaling pathways to apoptosis and marrow fibrosis were not defined in this study. These features were, however, substantially rescued by either a catecholaminergic agonist or the natural Il-1 receptor antagonist Il-1ra, establishing essential roles of both Il-1 and sympathetic denervation in bone marrow pathophysiology caused by Jak2 V617F.
