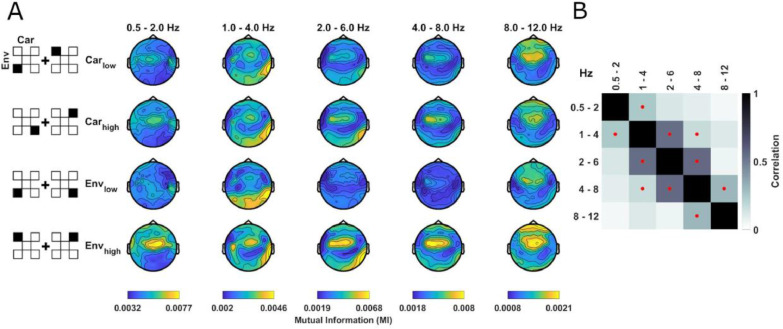
Fig. 2.
Specificity and spatial topographies of envelope tracking. (A) Condition-averaged topographies of envelope tracking, quantified as mutual information (MI), separately for the factors low/high carrier bands (Carlow, Carhigh) and low/high envelope ranges (Envlow: 0.2 - 0.83 kHz, Envhigh: 2.66 - 8 kHz) in block 1. To create the analysis factors, the MI values were averaged across the respective other dimension (e.g. over envelope bands for Carlow, Carhigh), as indicated by the pictograms on the left. These tracking signatures were significant for each envelope and carrier when compared with a bootstrap distribution reflecting the null hypothesis of no systematic relation between EEG and stimulus (see main text). Color ranges are fixed within each EEG band. (B) Spatial similarity (Pearson correlation) of group-level MI topographies between EEG bands (averaged over conditions). Red dots indicate a significant (p<0.01) one-sided group-level bootstrap test against zero.