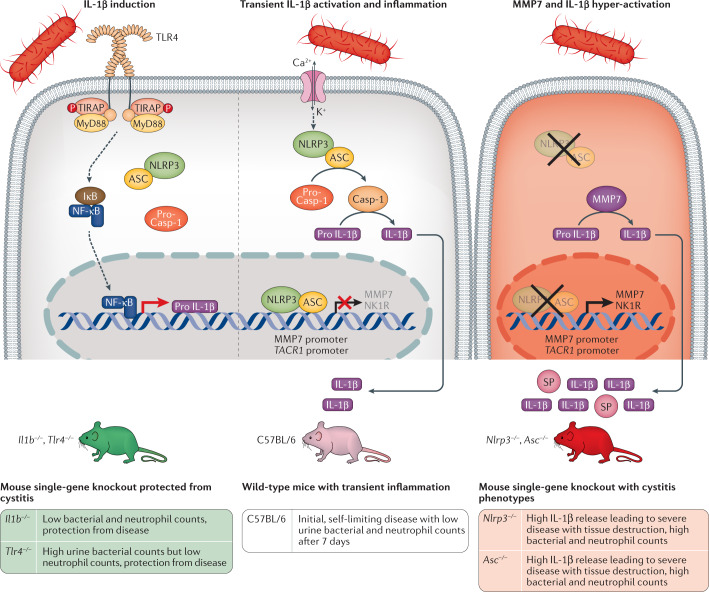
Fig. 7. Host determinants of disease severity in acute cystitis; mechanism of IL-1β and SP hyperactivation.
Acute cystitis is a disease caused by excessive inflammation in the urinary bladder, accompanied by pain, frequency of micturition and urgency. The molecular basis of disease is illustrated here, focusing on the host determinants of disease and especially the IL-1β response. Left panel: bacteria engage urothelial cell receptors and trigger the expression of pro-IL-1β by activating Toll-like receptor 4(TLR4) signalling through the MyD88 adaptor pathway and the transcription factor NF-κB. IL-1β is essential for disease pathogenesis, as shown by the protection from acute cystitis in Il1b−/− and Tlr4−/− mice, which lack the pro-IL-1β response to infection with uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) strains. Middle panel: bacteria activate the NLRP3 inflammasome via a second signal involving mechanisms such as ion fluxes. Activated caspase 1 (Casp-1) then cleaves pro-IL-1β to its mature and active form. The release of IL-1β triggers inflammation in the bladder and creates transient, mild disease in C57BL/6 wild-type mice. Right panel: in inflammasome-deficient mice an alternative IL-1β-processing mechanism takes over. Mice lacking the NLRP3 inflammasome owing to single gene deletions (Asc−/− or Nlrp3−/− mice) develop an IL-1β hyper-activation syndrome explained by excessive processing by matrix metalloproteinase 7 (MMP7)33. In addition, ASC and NLRP3 regulate the expression of the pain receptor neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R; encoded by TACR1), by acting as transcriptional repressors of both MMP7 and TACR1. ASC and NLRP3, therefore, act as molecular gatekeepers, defining the level of transcription of the pro-inflammatory response driven by pro-IL-1β, and the pain response, driven by NK1R and substance P (SP). In Asc-deficient or Nlrp3-deficient mice, in which this gatekeeping function is lost, UPEC-infected mice develop severe acute cystitis, mediated by excessive MMP7 cleavage of pro-IL-1β and by over-production of NK1R33,35. ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; IκB, inhibitor of κB; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; P, phosphate group; TIRAP, Toll/interleukin 1 receptor-domain-containing adaptor protein. Adapted from ref.33, CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).