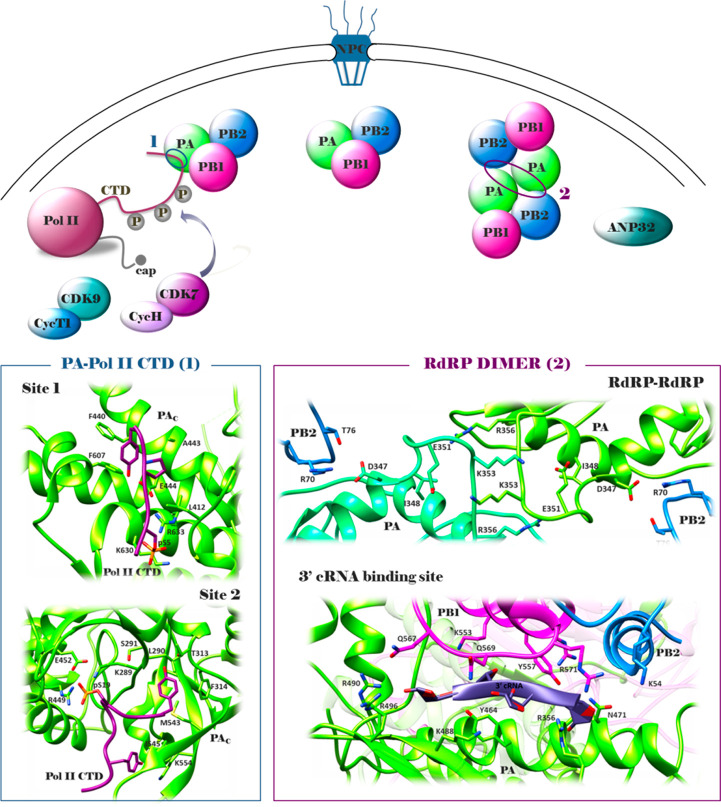
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the flu RdRP association with Pol II during vRNA transcription and dimerization during vRNA replication (upper side): once heterotrimerization has occurred in the nucleus, RdRP performs both the processes of transcription and replication; during transcription of viral mRNA, the specific interaction between the PAC and host Pol II CTD is required to enable the process of cap-snatching; during replication, a new RdRP is synthesized and associates with the resident RdRP to form a dimer, which is required for the synthesis of cRNA from vRNA (interactions occurring between the PAC loop of the two RdRPs and PAC of one RdRP and PB2 loop of the other); finally, the association of PB2 and host factor ANP32 promote the replication of vRNA from cRNA (interaction occurring at the PB2 627 domain). For clarity, the RdRP is shown alone and not in the context of the vRNP. Crystal structures of the PA–Pol II CTD interface (pdb: 5M3H(81)), RdRP–RdRP interface (pdb: 6QPG(33)), and 3′ cRNA binding site (pdb: 6QX3(33)) (lower side). PA subunit, green; PB2 subunit, blue; PB1 subunit, magenta. The figure is author created, and the structures have been adapted from the pdb mentioned above and drawn by using the UCSF Chimera package.47