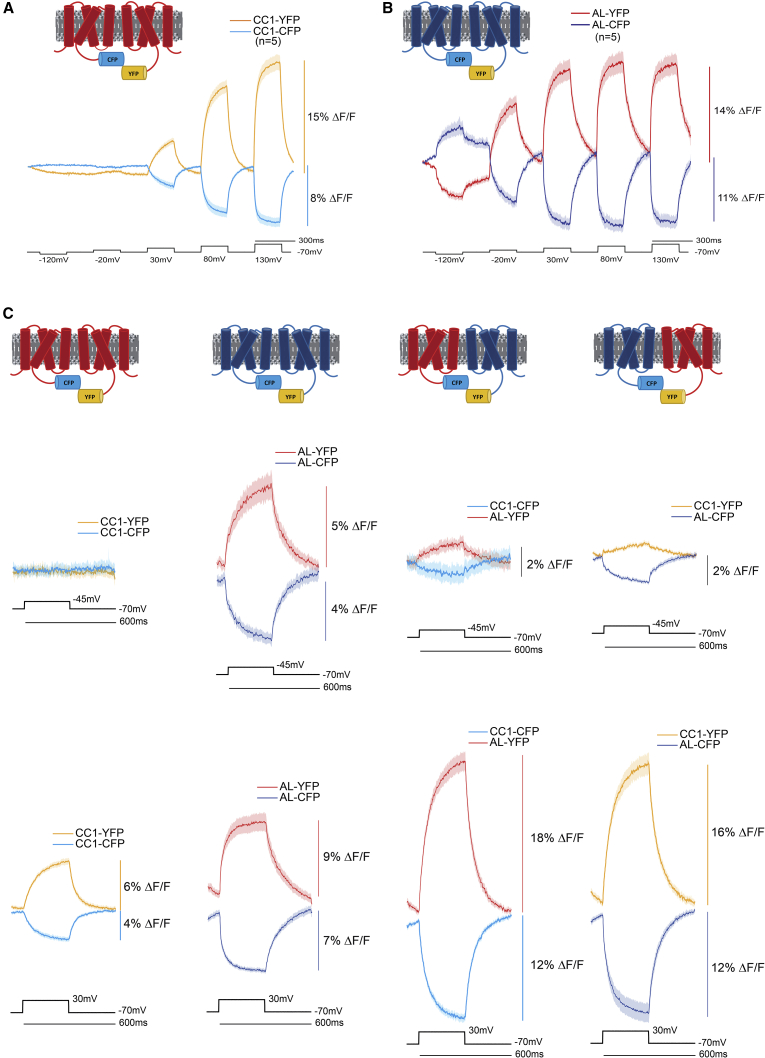
Figure 6.
Decoupling the voltage-dependent FRET signal by varying the voltage sensitivities of the voltage-sensing domains. (A) An inter-FRET GEVI pair using the voltage-sensing domain from CC1 (red transmembrane segments) that has a positively shifted voltage responsive range. The donor fluorescence trace is in light blue (CC1-CFP). The acceptor fluorescence trace is in yellow (CC1-YFP). Voltage steps are in black. (B) An intermolecular FRET GEVI using the voltage-sensing domain from ArcLight (blue transmembrane segments) that responds to more negative membrane potentials. The donor fluorescence trace is in dark blue (AL-CFP). The acceptor fluorescence trace is in red (AL-YFP). (C) Four columns of the different combinations of CC1 and ArcLight inter-FRET GEVI pairs. The top row of traces are from HEK cells experiencing a 25 mV depolarization of the plasma membrane potential. The bottom row of traces are from HEK cells experiencing a 100 mV depolarization of the plasma membrane potential. The colors of the traces and voltage-sensing domains are as described in (A) and (B). Excitation wavelength was 430 nm for all experiments. CFP emission was measured at 480 nm, and YFP emission was measured at 540 nm. All traces are the averages from six cells. The solid line in the traces represents the mean and the shaded area is the standard error of the mean.