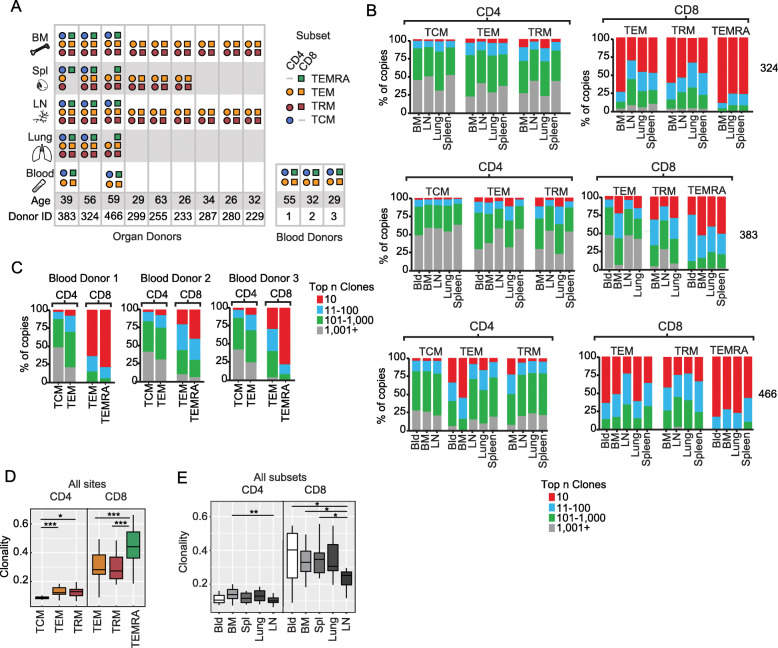
Fig. 1.
T cell receptor (TCR) diversity of memory cells is coupled to lineage and subset identity. A Tissue and subset origin of samples analyzed in this study derived from 12 individuals. T cell subsets included TEM (effector memory) and TRM (resident memory) for CD4+ and CD8+T cells, CD4+TCM (central memory), and CD8+TEMRA (terminally differentiated effector), isolated from blood, bone marrow (BM), spleen (Spl), lymph node (LN, lung-draining), and lungs of organ donors; TEM, TCM, and TEMRA cells were isolated from blood of three living donors. B Clonal expansion plots show proportion of top n clones per sample for CD4+ (left) and CD8+ (right) T cell subsets (TCM, TEM, TRM, and TEMRA) from indicated sites for three representative organ donors (donor number is given on the right). C Clonal expansion plots as in B for each of the three blood donors. The same clone rank legend (bar color scale) applies to both B and C. D TCR clonality was calculated (see methods) for each subset from all sites and donors in A. Boxplot depicts clonality by cell subset (all tissue sites combined) as 25% quantile (lower), median (middle), and 75% quantile (upper) and whiskers at minimum and maximum values. (CD4+: TCM, n = 15 TEM, n = 32; TRM, n = 27; CD8+: TEM, n = 31; TRM, n = 26; TEMRA, n = 14). E Clonality of T cells (calculated as in D stratified by tissue site (all subsets combined) (CD4+: Bld, n = 10, BM, n = 21; Spl, n = 14; Lung, n = 8; LN, n = 21; CD8+: Bld, n=10; BM, n = 21; Spl, n = 13; Lung, n = 9; LN, n = 18). Students t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001