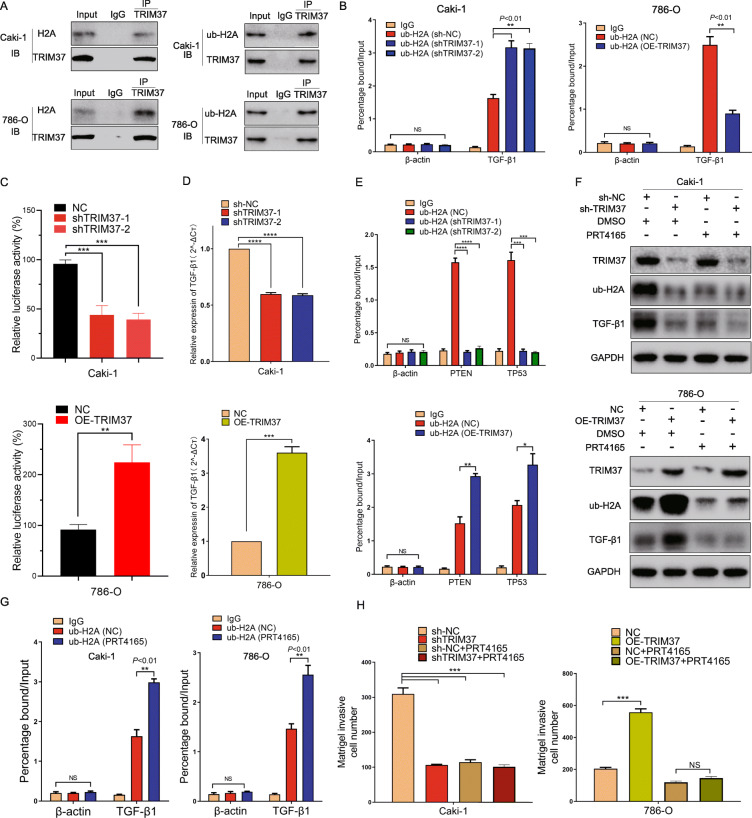
Fig. 5.
TRIM37 activating TGF-β1 signaling in RCC progression requires histone H2A ubiquitinated modification. A, TRIM37 directly interacted with histone H2A and ub-H2A in RCC cells with immunoprecipitation assay. B, Ablation of TRIM37 significantly improved ub-H2A levels at the TGF-β1 promoter site in Caki-1 cells, while overexpressing TRIM37 in contrast decreased ub-H2A enrichments in 786-O cells. C, knockdown of TRIM37 significantly reduced the luciferase activity of TGF-β1 of Caki-1 cells, overexpression of TRIM37 on the contrast enhanced its activity. D, TGF-β1 mRNA level decreased or elevated in knockdown or overexpressing TRIM37 models, respectively. E, TRIM37 knockdown significantly reduced ub-H2A occupancy at the promoter sites of PTEN and TP53 in Caki-1 cells, indicating the decreasing repression of transcription, while overexpressing TRIM37 showed opposite effects in 786-O cells. F, Specific ub-H2A inhibitor PRT4165 significantly abolished H2A ubiquitinating levels, TGF-β1 expression in sh-NC or sh-TRIM37 cell models, with TRIM37 expression no change, indicating that TRIM37 functioned at the upstream of both H2A and TGF-β1. In TRIM37 overexpression cells, PRT4165 could obviously inhibited ub-H2A and TGF-β1 expression, which were upregulated by TRIM37. G, PRT4165 could increase the occupancy of ub-H2A at TGF-β1 promoter site in Caki-1 and 786-O lines, which is similar to TRIM37 ablation. H, PRT5165 significantly restrained the invasive capabilities of cells with TRIM37 knockdown or overexpression, indicating the functional effects of ubiquitinating inhibition