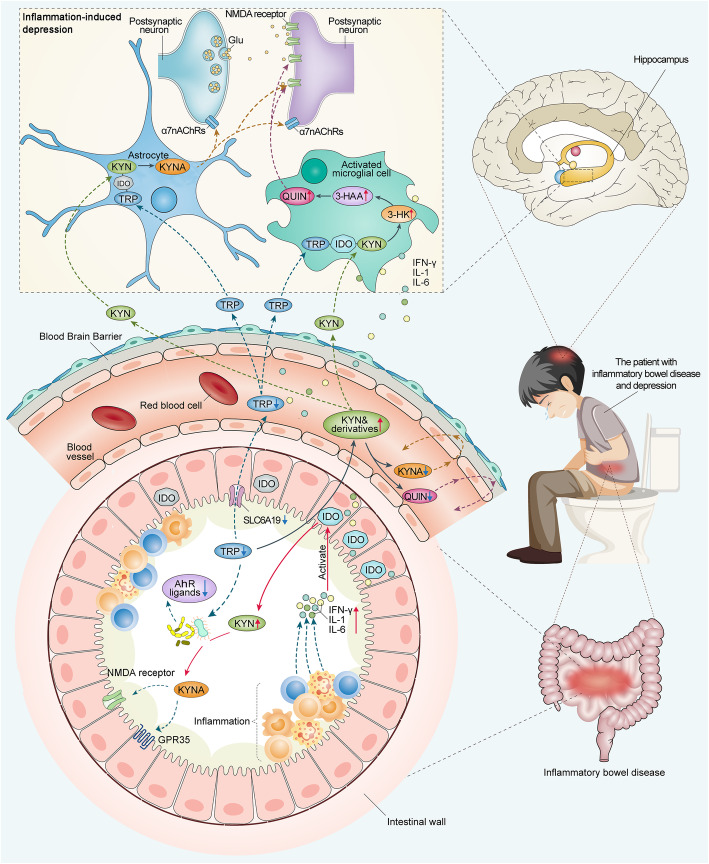
Fig. 2.
The link between intestinal inflammation, KP, and depression in IBD. In the process of IBD, inflammatory activity stimulates intestinal cells to produce a series of inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-1. Activation of IDO by inflammatory cytokines results in increased degradation of TRP to KYN, which crosses the blood-brain barrier and is metabolized by different branches to QUIN and KYNA. In an inflammatory environment, a higher rate of production of neurotoxic molecules such as QUIN, 3-HK, and 3-HAA may cause depression by damaging hippocampal neurons. In contrast, KYNA is a neuroprotective factor. These KP metabolites affect the mood of IBD patients through a complex series of neurobiological responses. IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; α7nAChRs, α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors; Glu, glutamate; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate