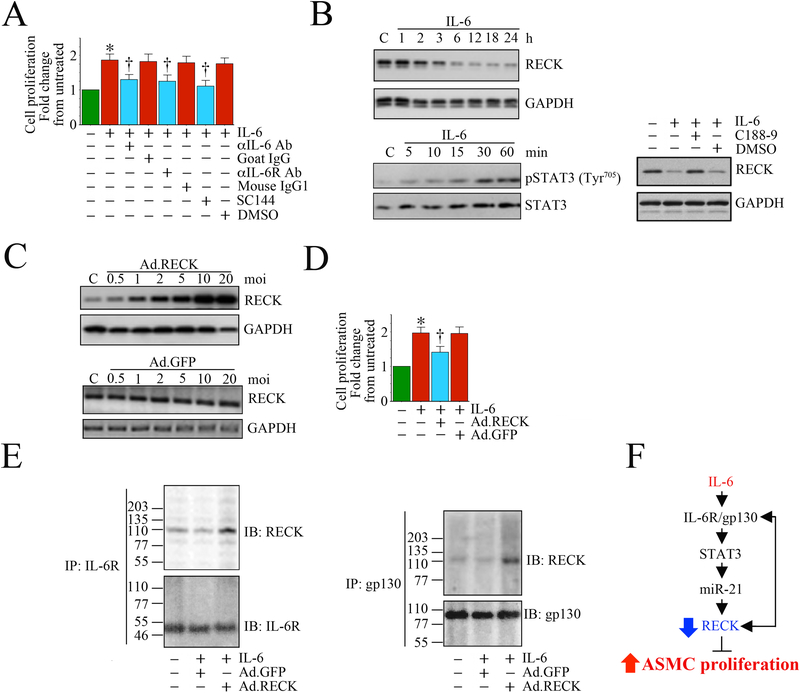
Fig. 5: Ectopic expression of RECK suppresses IL-6 mediated aortic smooth muscle cell (ASMC) proliferation. RECK physically associates with IL-6R and gp130.
A, Recombinant human IL-6 induces human ASMC (SMC) proliferation. SMC were grown in SmGM-2 medium, and at 70% confluency, the culture medium was replaced with basal medium containing 0.5% BSA (conditioning medium). After 48 h incubation, the quiescent SMC were incubated with IL-6 (10 ng/ml) for 48 h and analyzed for proliferation by CyQuant assay (n=6). Specificity of IL-6 was verified by incubating quiescent SMC with neutralizing IL-6 or IL-6R antibody (10 mg/ml for 1 h) or the gp130-specific inhibitor SC144 (5 μM in DMSO for 24 h) prior to IL-6 addition (n=6). B, IL-6 suppresses RECK via STAT3 activation. Quiescent SMC were incubated with IL-6 (10 ng/ml) for the indicated time periods. In a subset of experiments, SMC were incubated with the STAT3 inhibitor C188–9 (10 mM in DMSO for 15 min) prior to IL-6 addition (10 ng/ml for 6 h). RECK expression (upper panel) and STAT3 phosphorylation (lower panel) were analyzed in cleared whole cell homogenates (20 μg) by Western blotting. GAPDH and total STAT3 served as loading controls. C, Adenoviral transduction of RECK (upper panel), but not control GFP (lower panel), increases RECK expression in a dose-dependent manner. Quiescent SMC were transduced with Ad.RECK (upper panel) or Ad.GFP (lower panel) at the indicated multiplicity of infection (moi) for 24 h. RECK protein expression was analyzed by Western blotting. D, Forced expression of RECK inhibits IL-6-induced SMC proliferation. SMC were transduced with Ad.RECK or Ad.GFP (moi10 for 24 h) were treated with IL-6 (10 ng/ml for 48h) and analyzed for proliferation as in A (n=6). E, RECK physically associates with IL-6R and gp130. SMC transduced with Ad.RECK or Ad.GFP and then treated with IL-6 were analyzed for IL-6R/RECK and gp30/RECK association by immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunnoblotting (IB) using soluble membrane fractions. F, Schematic showing the signaling pathway involved in IL-6/IL-6R/gp130-mediated STAT3 activation, RECK suppression and SMC proliferation. Importantly, forced expression of RECK suppressed IL-6-mediated SMC proliferation. Double head arrow: Physical association of RECK with IL-6R or gp130. *P<0.05 vs. untreated, †P<0.05 vs. IL-6.