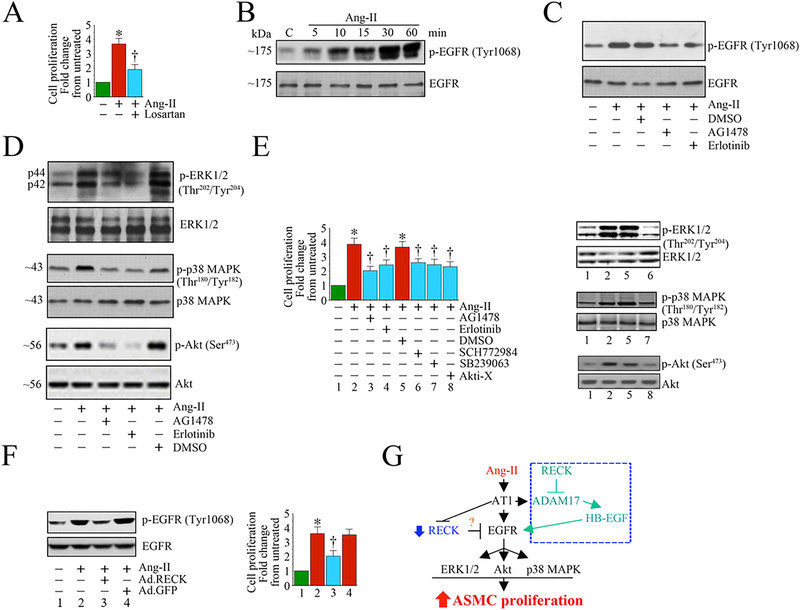
Fig. 6:
Ectopic expression of RECK suppresses Angiotensin (Ang)-II-induced human aortic smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation by inhibiting EGFR activation. A, Angiotensin (Ang)-II stimulates SMC proliferation via AT1. Quiescent SMC were incubated with the AT1 antagonist Losartan potassium (10 μM) for 1 h prior to Ang-II addition (100 nM for 48 h). Cell proliferation was analyzed by CyQuant assay (n=6). B, C, Ang-II induces EGFR activation in a time-dependent manner and is inhibited by AG1478 and erlotinib. Quiescent SMC treated with Ang-II were analyzed for EGFR activation by Western blotting using cleared whole cell lysates and activation-specific antibodies. Total EGFR served as a loading control. In a subset of experiments (C), quiescent SMC were treated with the EGFR-specific inhibitors AG1478 (100 μM in DMSO for 30 min) or erlotinib (1 μM in DMSO for 1h) prior to Ang-II (100 nM for 30 min). D, E, Ang-II induces SMC proliferation via EGFR-dependent ERK½, p38 MAPK and Akt activation. Quiescent SMC were treated with AG1478 or erlotinib prior to Ang-II addition (100 nM for 1 h). Activation of ERK½, p38 MAPK, and Akt were analyzed by Western blotting using cleared whole cell lysates and activation-specific antibodies (D). In a subset of experiments, quiescent SMC incubated with EGFR inhibitors AG1478 or erlotinib, the ERK½ inhibitor SCH772984 (10 μM in DMSO for 1h), p38 MAPK inhibitor SB239063 (10 μM in DMSO for 1h) or the Akt inhibitor Akti-X (1 μM in DMSO for 1h) prior to Ang-II addition (100 nM for 48 h) were analyzed for proliferation as In A (E). The efficacy of inhibitors on respective target proteins was analyzed by Western blotting as shown on the right. F, Ectopic expression of RECK inhibits Ang-II-induced EGFR activation. SMC transduced with Ad.RECK or control GFP were incubated with Ang-II (100 nM for 30 min) were analyzed for EGFR activation by Western blotting (left hand panel). In a subset of experiments, SMC transduced with Ad.RECK or Ad.GFP were made quiescent, treated with Ang-II (100 nM for 48 h) and then analyzed for proliferation (right hand panel). G, Schema showing possible signaling pathways involved in Ang-II/AT1-mediated EGFR activation, RECK suppression and SMC proliferation. While Ang-II induced EGFR activation, it suppressed RECK expression. Further, targeting EGFR inhibits Ang-II-induced ERK½, Akt and p38 MAPK activation, and ASMC proliferation. Importantly, ectopic expression of RECK suppresses EGFR activation and inhibits Ang-II-induced SMC proliferation. RECK suppresses EGFR activation without physical association (data not shown), suggesting that RECK-mediated suppression of EGFR activation is indirect, and may involve (hypothesis) RECK inhibition of Ang-II/AT1/ADAM17-mediated cleavage and release of EGFR ligands such as HB-EGF from the cell surface, and binding to EGFR (blue box at the top right). *P<0.05 vs. untreated, †P<0.05