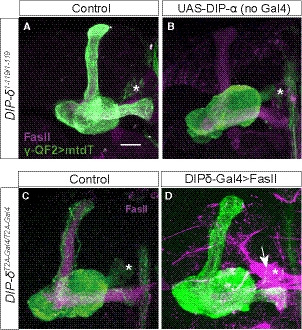
Figure EV6. UAS‐DIP‐α function is Gal4‐dependent; FasII overexpression fails to suppress the DIP‐δ mutant phenotype, related to Fig 8.
-
A, BConfocal z‐projections of DIP‐δ1‐119 homozygous mutant brains, in which γ‐KCs are labeled by membrane‐bound tandem tomato (mtdT‐HA; green) driven by R71G10‐QF2 (γ‐QF2), that either contain (B) or do not contain (A) a UAS‐DIP‐α transgene.
-
C, DConfocal z‐projections of DIP‐δT2A‐Gal4/T2A‐Gal4 homozygous mutant brains, in which γ‐KCs are labeled by mtdT‐HA (green) driven by γ‐QF2, that either express (D) or do not express (C) a UAS‐FasII transgene driven by DIP‐δ‐Gal4.
Data information: Magenta is FasII; arrow in (D) indicates FasII accumulation in DIP‐δ+ PAM‐DANs. Asterisks mark the distal edge of the lobe. Scale bar is 20 µm.
