Figure 7.
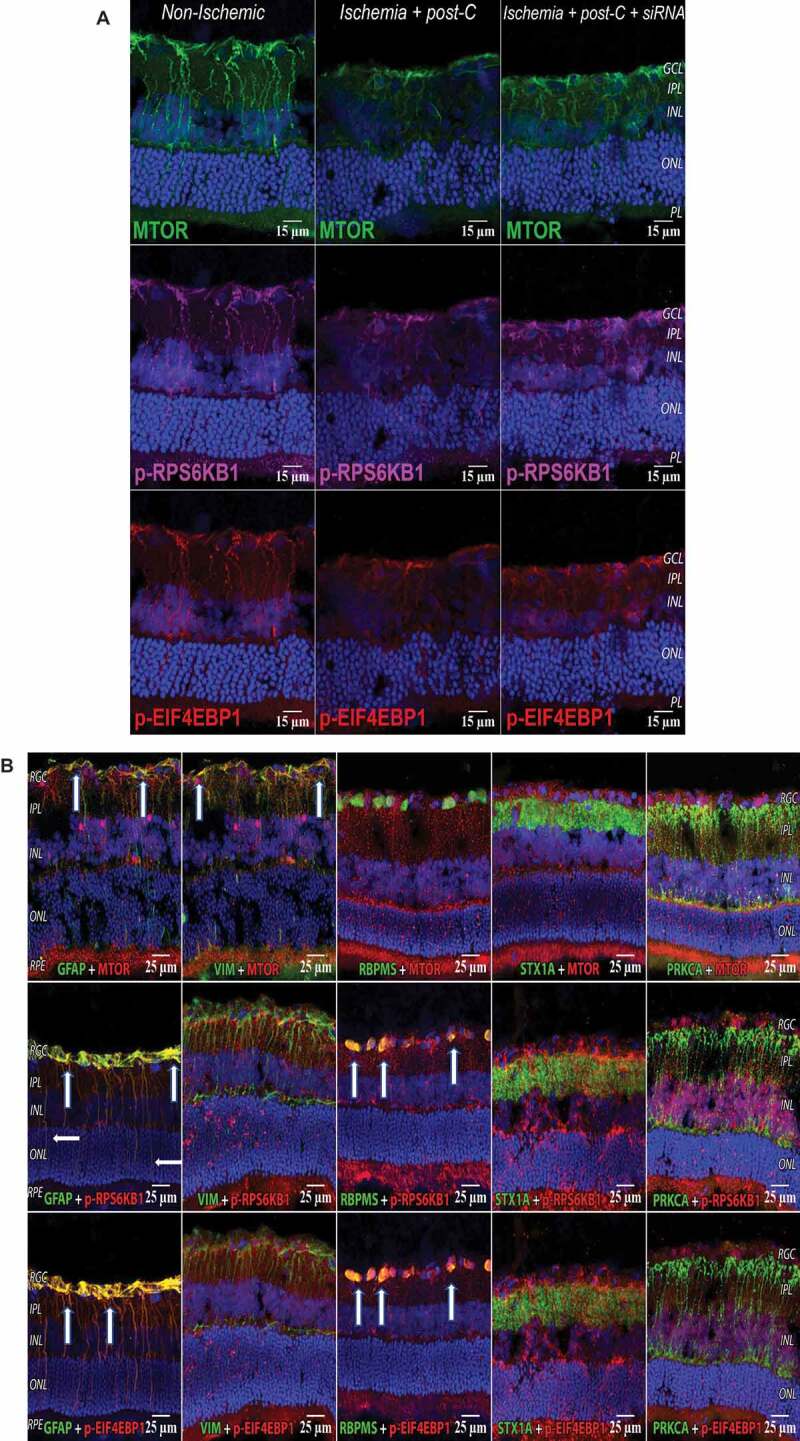
MTOR pathway in retina with ischemia and post-C. (A) Changes in immunostaining for the MTOR pathway (from left to right) in normal, ischemia + post-C + scrambled, and ischemia + post-C + Atg5 siRNA. Retinal cryosections were prepared 24 h after post-C (that is, 48 h after ischemia), and examined using confocal microscopy. From top to bottom are staining for MTOR, p-RPS6KB1, and p-EIF4EBP1. These are representative images from N = 3 per group. Orientation is shown on far right; magnification 40x. (B) Localization of MTOR pathway proteins in retinal cells. These cryosections are all taken from the same group, ischemia + post-C + scrambled Atg5 siRNA, at 24 h after post-C (that is, 48 h after ischemia). Nuclei were stained blue using DAPI. From top to bottom are staining (red) for MTOR, p-RPS6KB1, and p-EIF4EBP1. From left to right (staining green) are: GFAP (Muller cells); VIM (for astrocytes); RBPMS (retinal ganglion cells); STX1A (amacrine cells); PRKCA (bipolar cells). For GFAP, white arrows indicate yellow overlap of MTOR (red), p-RPS6KB1: red; and p-EIF4EBP1: red with GFAP: green, in Muller cell endplates and projections. For VIM, white arrows indicate yellow overlap of MTOR (red) and VIM (green) in the superficial inner retina. For RBPMS, white arrows indicate yellow overlap of p-RPS6KB1: red, and p-EIF4EBP1: red with RBPMS: green in retinal ganglion cells. There was no evident overlap with the MTOR pathway for STX1A (amacrine cells), and PRKCA (bipolar cells). Orientation on far left. RGC = retinal ganglion cells, IPL = inner plexiform layer, INL = inner nuclear layer, ONL = outer nuclear layer, RPE = retinal pigment epithelium. Representative images from N = 3 per group; magnification 40x
