Figure 10.
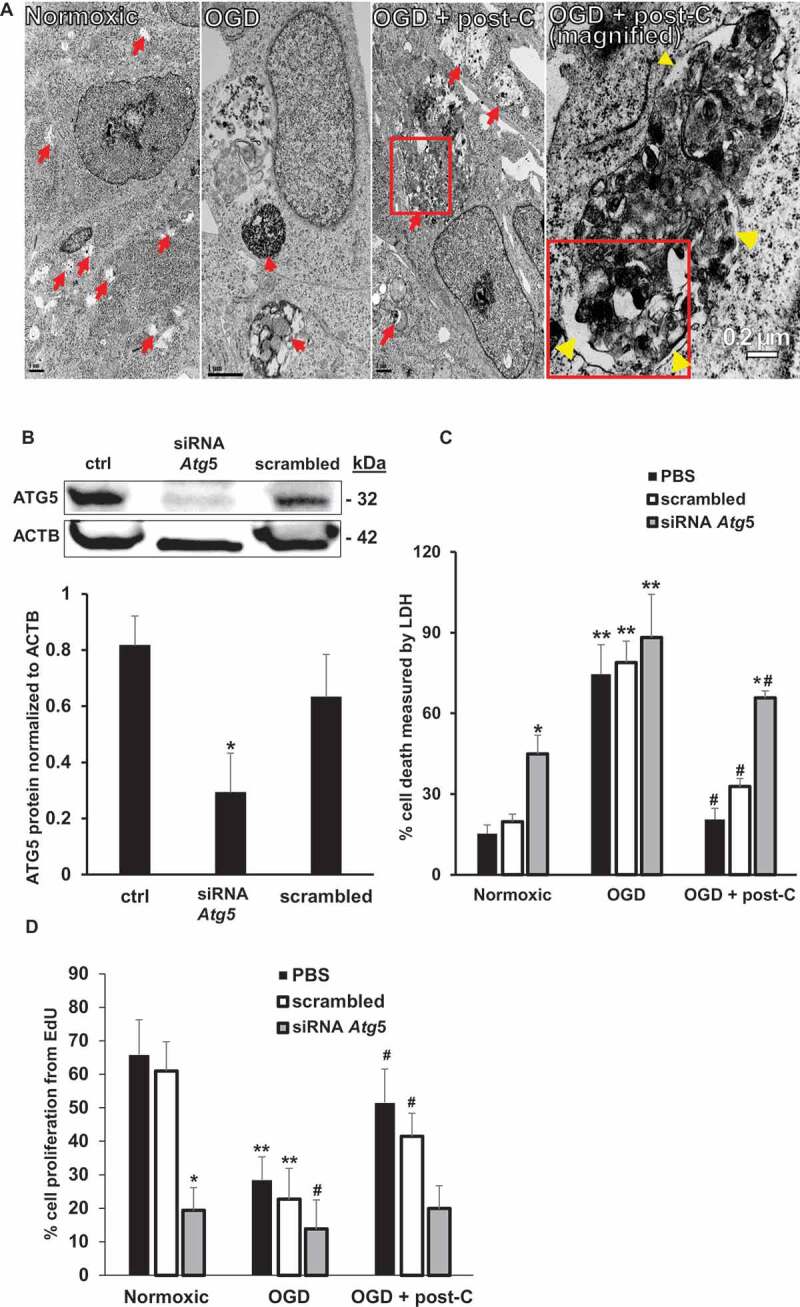
Blockade of Atg5 attenuates post-C-mediated neuroprotection in R28 cells subjected to OGD in vitro. (A) EM evidence of autophagy induction by post-C in R28 retinal neuronal cells. Electron micrographic images of autophagosomes in R28 cells subjected to normoxia, OGD and OGD + post-C. Red arrows point to autophagosomes. With OGD, autophagosomes appeared densely packed with cellular material. When post-C was added, the autophagosomes were larger in size, and less densely packed compared to OGD. Yellow arrowheads in the magnified image (far-right) inside and outside the boxed area indicate double membranes. Scale bar = 1 µm except for right-most image at 0.2 µm. (B) Representative western blot illustrating the silencing efficiency of Atg5 siRNA in R28 cells. The cells were treated with PBS (“control”), siRNA to Atg5, or scrambled. mean ± SEM; n = 4 per group; * = p < 0.05 siRNA Atg5 vs. control or scrambled. ACTB was loading control. (C) Atg5 silencing and cell death with normoxia, OGD, and OGD + post-C measured by LDH assay. mean ± SEM; n = 5 per treatment; * = p < 0.05 for scrambled or control vs. siRNA within groups; ** = p < 0.05 normoxia vs. OGD for each treatment; # = p < 0.05 OGD vs. OGD + post-C. (D) Atg5 silencing significantly altered proliferation in all three groups measured by EdU assay. mean ± SEM; n = 5 per treatment; * = p < 0.05 for scrambled or control vs. siRNA within groups; ** = p < 0.05 normoxia vs. OGD for each treatment; # = p < 0.05 OGD vs. OGD + post-C
