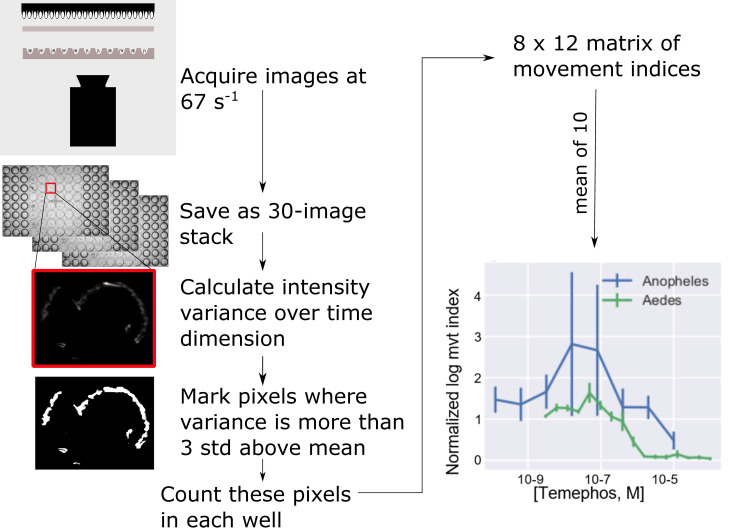
Fig 1. The procedure for automating the analysis of mosquito larval swimming.
In each trial, 30 images are acquired at 10 ms intervals and stored for later offline analysis. An index of the amount of movement is obtained by measuring the variance for each pixel over time. Pixels for which the variance more than 3 standard deviations from the mean variance are scored as 1, the remainder as 0. The movement index for each well is taken as the sum of these scores for that well. The output of the algorithm for quantifying movement plotted against the concentration of temephos (bottom right), a larvicide commonly used in the control of mosquitoes, is shown at the end of the pipeline. Alongside this similar data for larvae of An. gambiae are shown. A concentration-dependent inhibition of movement is seen in studies on larvae of An. gambiae and Ae. aegypti.