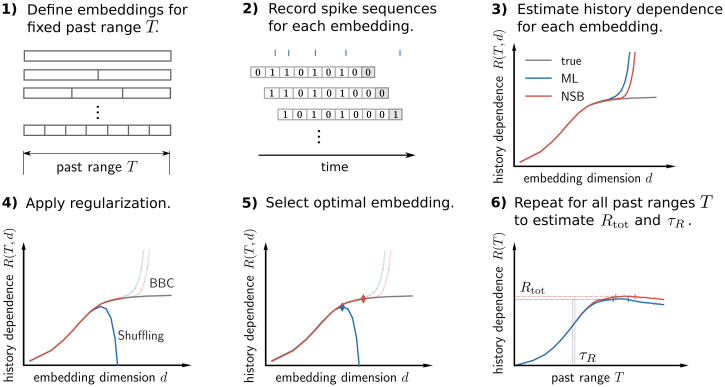
Fig 10. Workflow of past-embedding optimization to estimate history dependence and the information timescale.
1) Define a set of embedding parameters d, κ for fixed past range T. 2) For each embedding d, κ, record sequences of current and past spiking for all time steps tn in the recording. 3) Use the frequencies of the recorded sequences to estimate history dependence for each embedding, either using maximum likelihood (ML), or fully Bayesian estimation (NSB). 4) Apply regularization, i.e. the Bayesian bias criterion (BBC) or Shuffling bias correction, to ensure that all estimates are unbiased or lower bounds to the true history dependence. 5) Select the optimal embedding to obtain an embedding-optimized estimate of R(T). 6) Repeat the estimation for a set of past ranges T to compute estimates of the information timescale τR and the total history dependence Rtot.