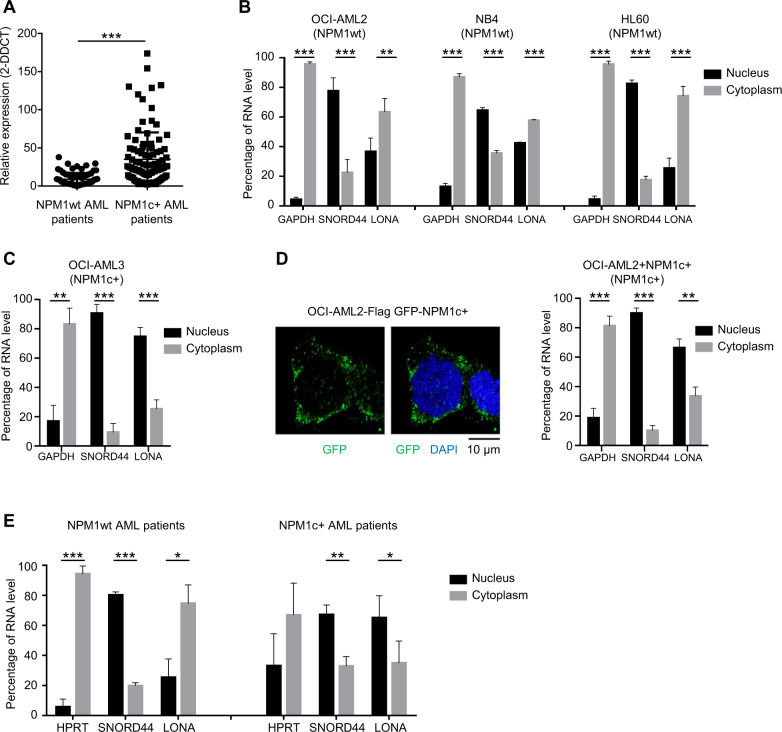
Fig. 1. Subcellular localization of the LONA lncRNA is dependent on the NPM1 mutational status.
A LONA lncRNA is overexpressed in NPM1 mutated AML patients. Relative expression of the LONA lncRNA between NPM1 wild type (NPM1wt) and NPM1 mutated (NPM1c + ) AML patients. The LONA RNA level of 174 patients (80 AML patients NPM1wt and 94 AML patients NPM1c + ) were evaluated by large scale quantitative real-time PCR (Fluidigm 96.96 Dynamic Array) [36]. Results were normalized to the expression of RNAseP, 5 S rRNA, and MLN51 and presented as relative expression [2-ddCt] ± Standard Deviation (SD). ***P < 0.001. B LONA is mainly cytoplasmic in NPM1wt OCI-AML2, NB4, and HL60 cell lines, and C LONA is nuclear in NPM1c + OCI-AML3 cells. RNA level of LONA lncRNA in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were evaluated by RT-qPCR after cell fractionation. Results are presented as percentage of RNA level. GAPDH was used as a positive control for cytoplasmic RNA fraction and SNORD44 was used as a positive control for nuclear RNA fraction. Bar graph represents the average from four independent experiments ± Standard Deviation (SD). **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001. Unpaired t-test. D Cytosolic localization of NPM1c + in the OCI-AML2 stably expressing Flag-GFP tagged NPM1c + (left). Cytospin cells were fixed and stained with DAPI. GFP fluorescence was examined with a confocal microscope. The mutant form of NPM1 leads to LONA nuclear delocalization (right). LONA RNA level in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were evaluated by RT-qPCR after cell fractionation of OCI-AML2 + NPM1c + cell line. Results are presented as percentage of RNA level. GAPDH was used as a positive control for cytoplasmic RNA fraction and SNORD44 was used as a positive control for nuclear RNA fraction. The bar graph represents the average from four independent experiments ± Standard Deviation (SD). **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001. Unpaired t-test. E LONA is cytoplasmic in NPM1wt AML patients and mainly nuclear in NPM1c + AML patients. RNA level of LONA lncRNA in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were evaluated by RT-qPCR after cell fractionation. Results are presented as percentage of RNA level. HPRT was used as a positive control for cytoplasmic RNA fraction and SNORD44 was used as a positive control for nuclear RNA fraction. Bar graph represents the average from three independent experiments ± Standard Deviation (SD). **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001. Unpaired t-test.