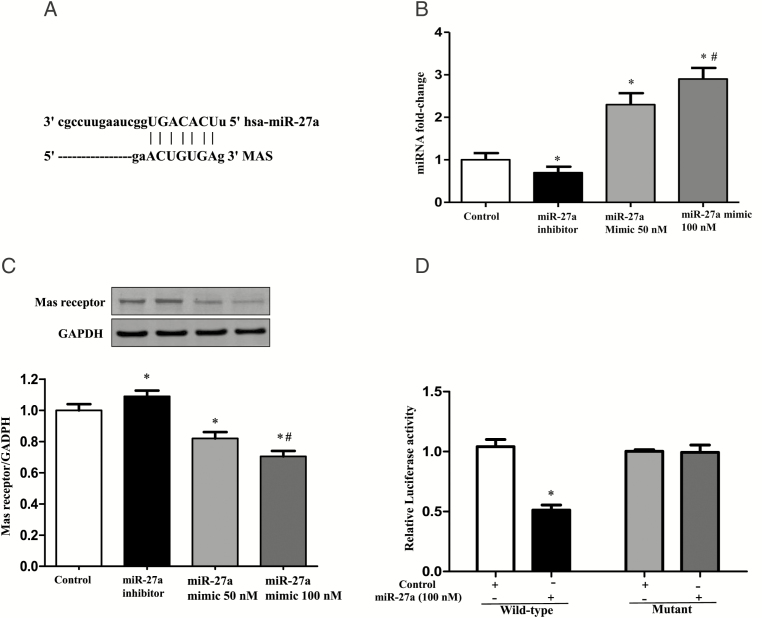
Figure 6.
Effect of monocyte miR-27a on the regulation of Mas receptor expression. (A) Genomic alignment showed of miR-27a binding site in the 3′-UTR of the Mas receptor predicted by TargetScan and miRTarBase softwares. (B) The expression of miR-27a in extracellular vesicles (EVs) from THP-1 cells treated with miR-27a inhibitor or mimic. EVs were collected from THP-1 cells transfected with miR-27a mimic (50 nM and 100 nM) or miR-27a inhibitor (100 nM) for 24 hours. The expression of miR-27a in EVs was quantified by qRT-PCR (n = 3/group, *P < 0.05 vs. Control, # P < 0.05 vs. 50 nM miR-27a mimic). (C) The protein expression of Mas receptor in HUVEC cells incubated with EVs from THP-1 cells transfected with miR-27a mimic and miR-27a inhibitor. THP-1 cells were transfected with miR-27a mimic (50 nM and 100 nM) and miR-27a inhibitor (100 nM) for 24 hours, and then EVs were collected, which were next incubated with the human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) for 24 hours. Mas receptor protein expression was quantified by immunoblotting (n = 3/group, *P < 0.05 vs. Control, #P < 0.05 vs. 50 nM miR-27a mimic). (D) Luciferase analysis of the effect of miR-27a mimic on the regulation of Mas receptor expression. Luciferase activity was measured in HEK-293 cells co-transfected with miR-27a, pMIR-MAS-3′-UTR (wild-type), or pMIR-MAS-3′-UTR (mutant) treated with vehicle (control) or miR-27 mimic (100 nM; n = 6/group, *P < 0.05 vs. control).