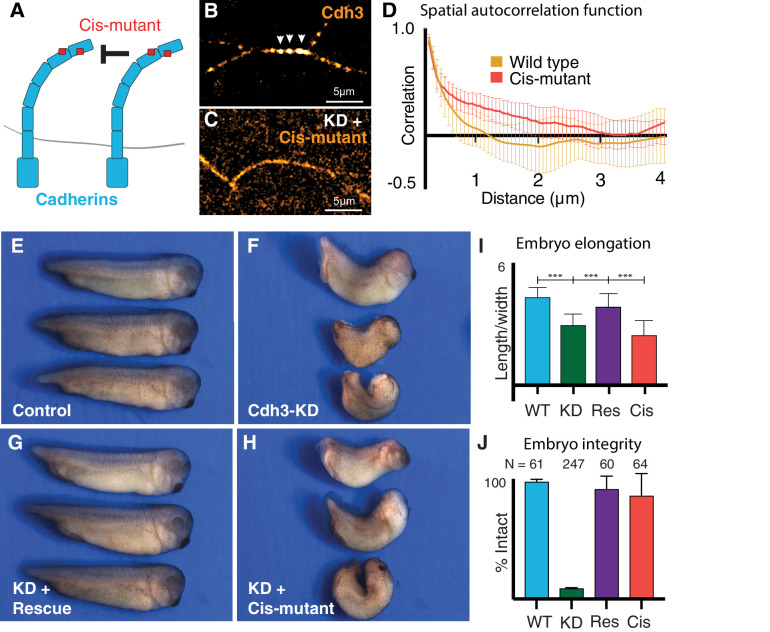
Figure 5. Cdh3 cis-clustering is required for convergent extension but not homeostatic tissue integrity.
(A) Mutations used to inhibit cadherin cis-clustering. (B) Cdh3-GFP clustering in a control embryo. (C) Cis-clusters absent after re-expression of cisMut-Cdh3-GFP. (D) Mean spatial autocorrelation of Cdh3-GFP intensity fluctuations for wild type (60 image frames, from 10 embryos) and the cis-mutant (56 image frames, five embryos) (Appendix, Section 17). Gradual, non-exponential decay for cisMut-Cdh3-GFP indicates a lack of spatial order (i.e. failure to cluster). (E) Control embryos (~stage 33). (F) Sibling embryos after Cdh3 knockdown. (G) Knockdown embryos re-expressing wild-type Cdh3-GFP. (H) Knockdown embryos re-expressing cisMut-Cdh3-GFP. (I) Axis elongation assessed as the ratio of anteroposterior to dorsoventral length at the widest point. (J) Embryo integrity assessed as percent of embryos alive and intact at stage 23.