Fig. 2.
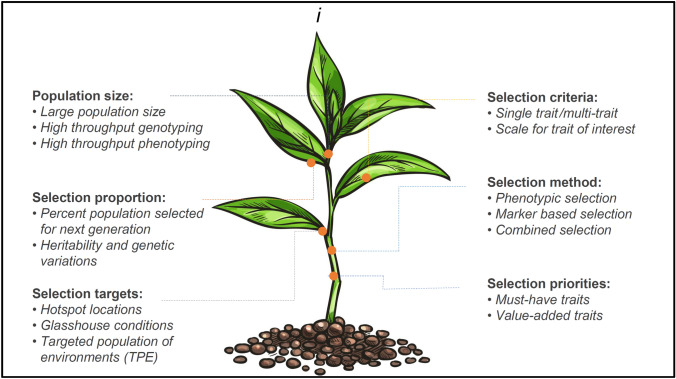
Enhancing selection intensity (i) through tweaking various parameters. For instance, the population size should be large enough to carry desirable recombinants for the trait of interest. As a matter of fact, the molecular markers can only be useful to identify the recombinants but cannot create recombinants into the populations. The effects of selection ratio (k) and phenotypic variation (standard deviation, σ) on selection differential also is an important factor. Selection targets can also be an important factor for the selection of traits including selection on hotspots, or selection in glasshouse conditions, and most importantly selection of traits in target population of environments (TPEs). High-throughput phenotyping and statistical designs can be useful to enhance selection intensity. Selection criteria is another important factor in which selection is based upon single or multiple traits and at the same time, the scale defined to characterize the traits is another important measure. Method of selection is a critical factor to increase the overall selection intensity which includes selection through trait-associated markers or a combination of phenotypic and genotypic selections. Another important basis for selection is the priorities of traits that can be characterized as must-have and value-added traits. In summary the selection intensity in breeding program depends upon the number of traits to be selected at the different stages, which requires rational budgeting of resources to handle populations with large sizes